Nocturnal animals are among nature’s most fascinating creatures, thriving in the darkness while the world around them sleeps. But what exactly are nocturnal animals, and why have some species evolved to be active only at night? Understanding these creatures and their unique adaptations can offer us a glimpse into the hidden world of nighttime animals, revealing the complex interplay between survival, evolution, and environment.
What Are Nocturnal Animals?
Nocturnal animals are species that are primarily active during the night and rest during the day. These animals have adapted to nighttime living through various means, allowing them to hunt, forage, and communicate in the dark. Unlike diurnal animals, which are active during daylight hours, nocturnal animals rely on their enhanced senses to navigate their environment when the sun sets.
Adaptations of Nocturnal Animals
Sensory Adaptations
One of the most remarkable features of nocturnal animals is their heightened senses. For instance, many nocturnal mammals have large eyes with a high concentration of rod cells, allowing them to see in low light. Owls, for example, can see up to 100 times better at night than humans, making them formidable nighttime hunters. In addition to superior night vision, many nocturnal animals possess exceptional hearing and smell. Bats, for instance, use echolocation, emitting high-frequency sounds that bounce off objects, helping them navigate and hunt in complete darkness.
Behavioral Adaptations
Nocturnal animals have also developed unique behaviors that help them thrive at night. Camouflage plays a vital role in the survival of nocturnal species, allowing them to blend into their surroundings and avoid predators. Animals like the leopard gecko have coloration that mimics the night environment, making them nearly invisible in the dark. Additionally, many nocturnal animals have developed specialized hunting techniques, such as the quiet, stealthy movements of cats or the precise strikes of a snake.
Why Do Animals Become Nocturnal?
There are several reasons why certain animals evolve to become nocturnal. Predation pressure is one significant factor; by being active at night, nocturnal animals can avoid daytime predators. Moreover, the cover of darkness provides a strategic advantage for predators themselves, as they can stalk and ambush their prey with less risk of detection.
Temperature regulation is another reason animals might be nocturnal. In harsh environments like deserts, where daytime temperatures can be extreme, being active at night allows animals to avoid the heat. For example, many desert mammals, such as the fennec fox, are nocturnal to stay cool and conserve water.
Nocturnal Animals List
Mammals
Bats:
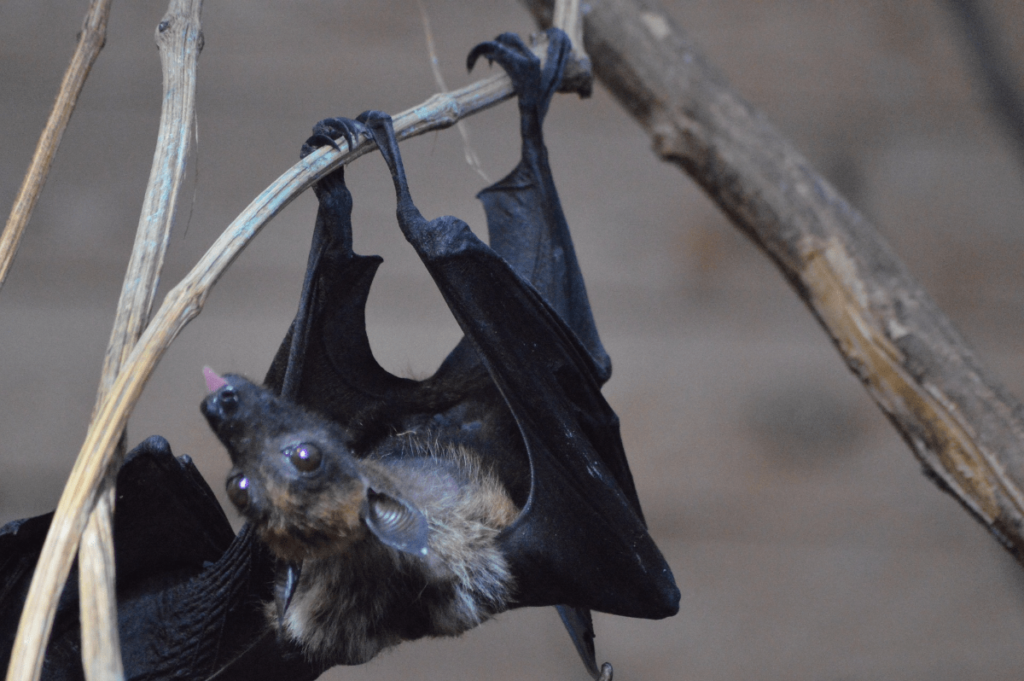

Bats are among the most diverse groups of nocturnal mammals. Fruit bats, such as the flying fox, use their keen sense of smell to find fruit in the dark, while vampire bats use thermal sensors in their nose to detect blood vessels in their prey. Insectivorous bats, like the pipistrelle, utilize echolocation to hunt insects in mid-air. This ability to navigate and hunt in complete darkness provides them a significant advantage over many other predators.
Raccoons:
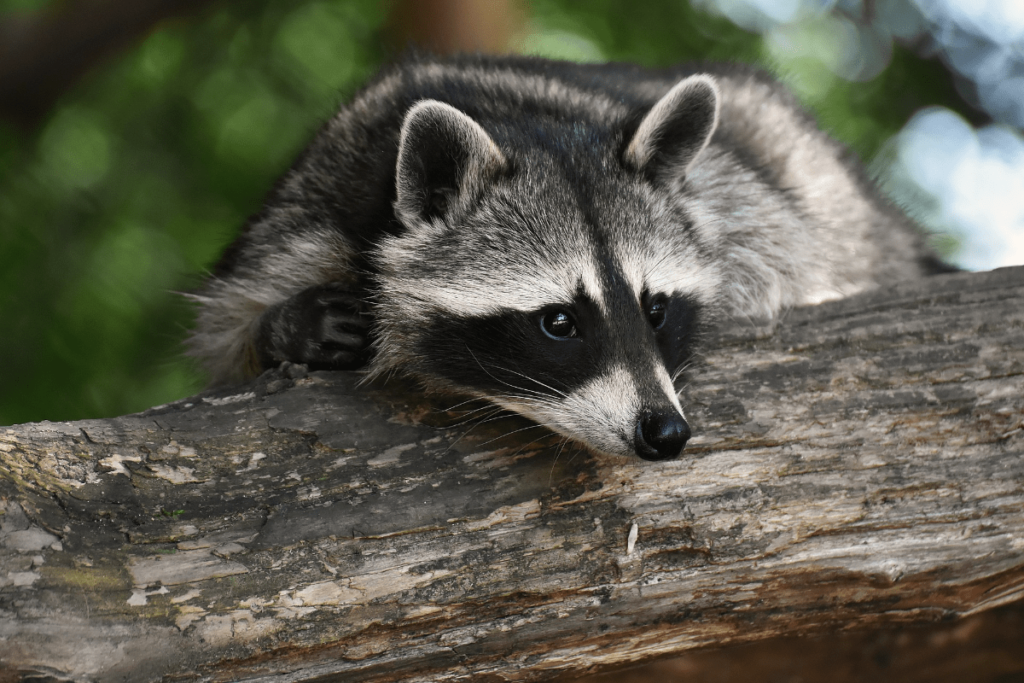

Raccoons are highly adaptable nocturnal mammals known for their dexterous front paws and masked appearance. They are omnivorous scavengers, feeding on a variety of foods including fruits, insects, and small animals. Their nighttime activity helps them avoid predators and human activity while scavenging for food. Raccoons are also notorious for their problem-solving skills, which they use to open containers and find food.
Owls:
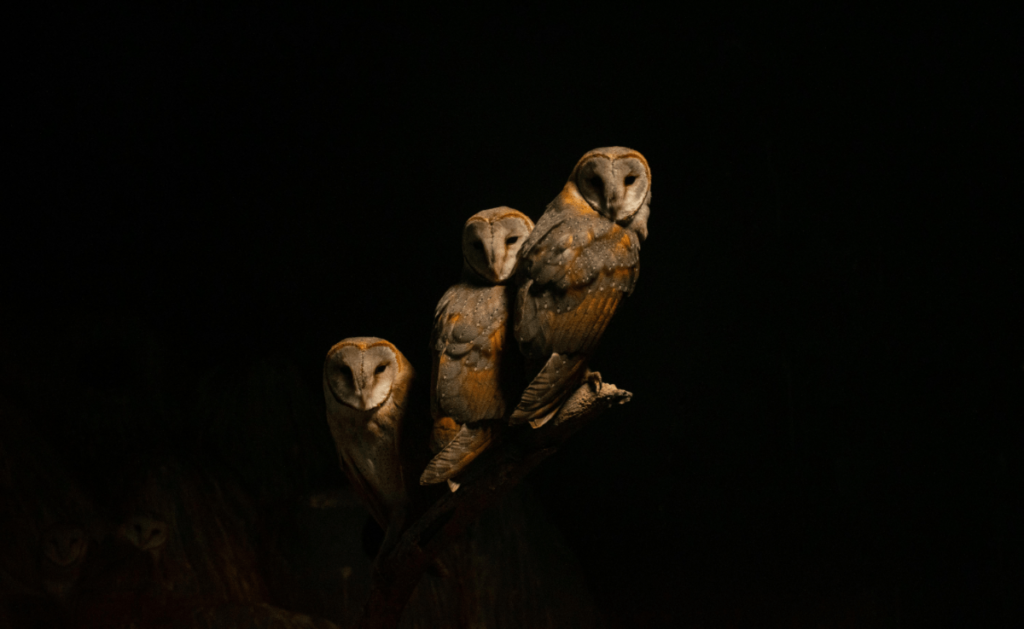

Owls are quintessential nocturnal birds of prey with specialized adaptations for hunting in low light. Their large, forward-facing eyes provide excellent night vision, while their silent flight allows them to approach prey without being detected. Owls have exceptional hearing, with some species able to pinpoint the location of their prey with remarkable accuracy. Their nocturnal nature helps them avoid competition with daytime birds of prey and take advantage of nighttime prey.
Learn about the impressive camouflage and physical traits of animals similar to those featured here in our article Camouflage Animals That Are Masters of Disguise in the Animal Kingdom
Opossums:
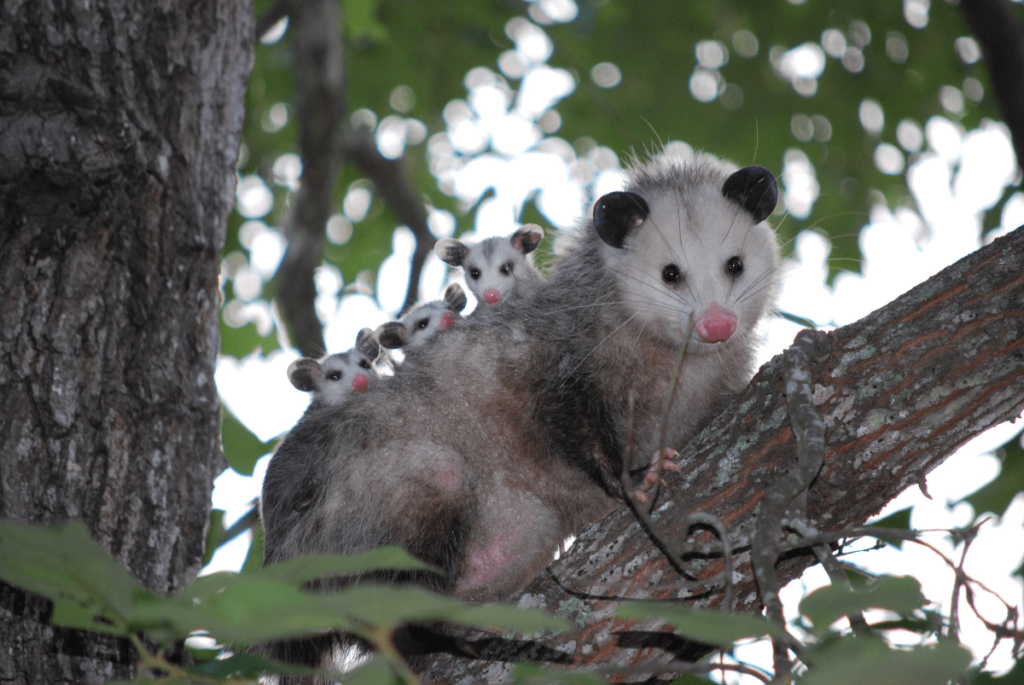

The Virginia opossum is a nocturnal marsupial with a range of survival strategies. They are scavengers, consuming a wide variety of foods from insects to carrion. When threatened, opossums display a unique defense mechanism by “playing dead,” which involves collapsing and emitting a foul odor to deter predators. Their nocturnal habits help them avoid predators and competition while foraging.
Hedgehogs:
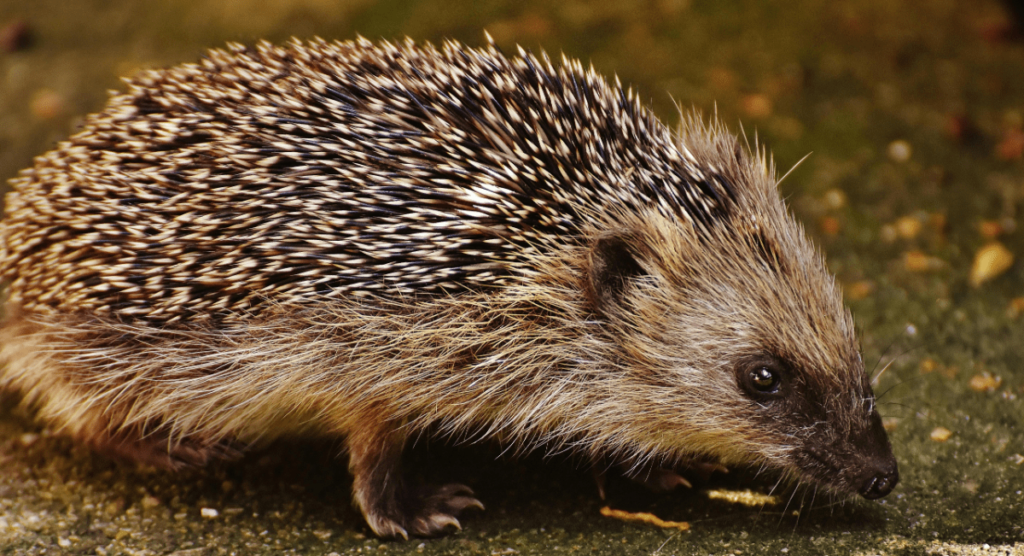

Hedgehogs are small, spiny mammals that emerge at night to forage for insects, worms, and other small invertebrates. Their nocturnal lifestyle helps them avoid daytime predators and exploit the abundant nighttime food resources. Hedgehogs have a unique defense mechanism—rolling into a tight ball to protect their vulnerable undersides from predators.
Aardvarks:
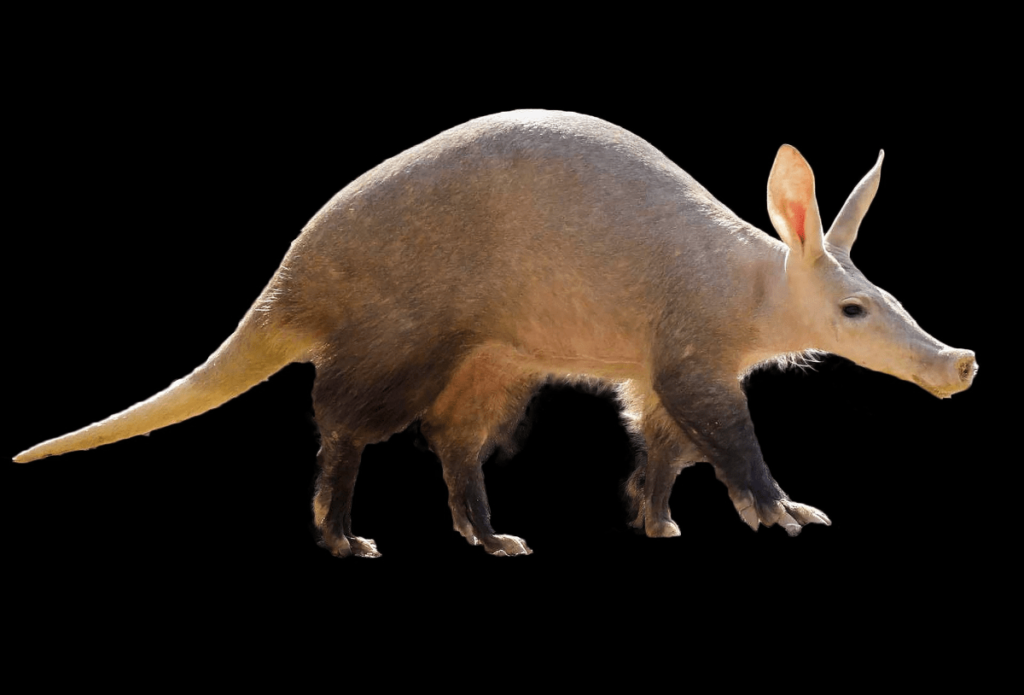

Native to Africa, aardvarks are nocturnal animals with a diet primarily consisting of ants and termites. Their nocturnal foraging helps them avoid the heat of the day and predators. Aardvarks use their strong claws to dig into ant hills and termite mounds, and their long, sticky tongue to extract insects. Their keen sense of smell allows them to locate insect colonies buried underground.
Fennec Fox:
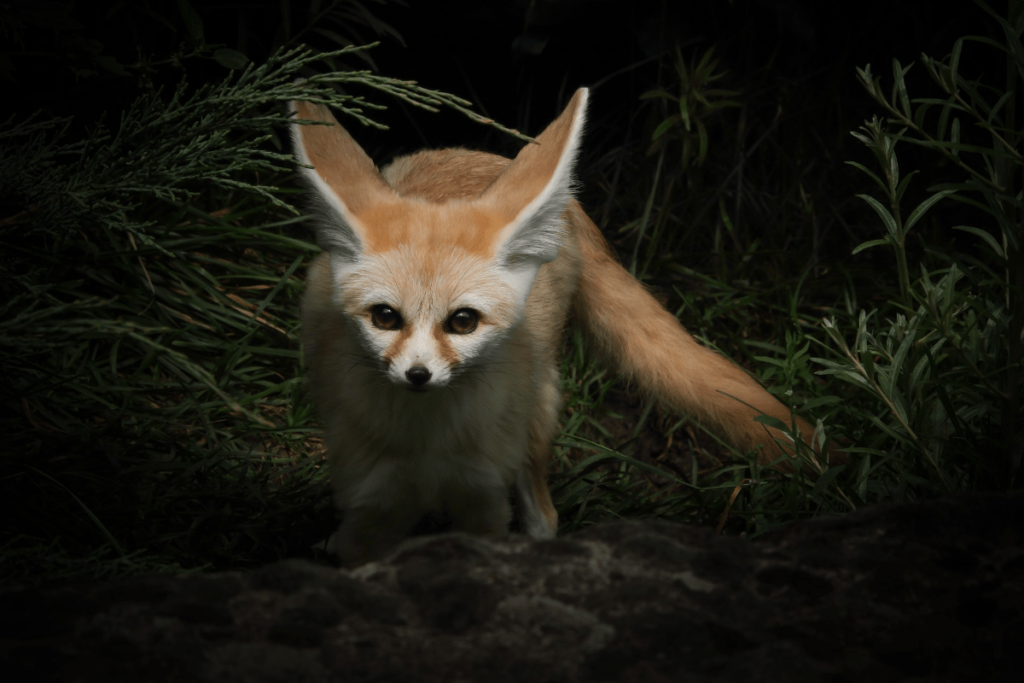

The fennec fox, with its large ears, is perfectly adapted to the desert environment. These nocturnal animals use their large ears to dissipate heat and detect prey such as insects, rodents, and small birds. Their nocturnal activity helps them avoid the extreme daytime temperatures of their desert habitat.
For more information on the Fennec Fox and other fascinating members of the canidae family, be sure to read our detailed guide on Canine Animals Family
Tasmanian Devil:
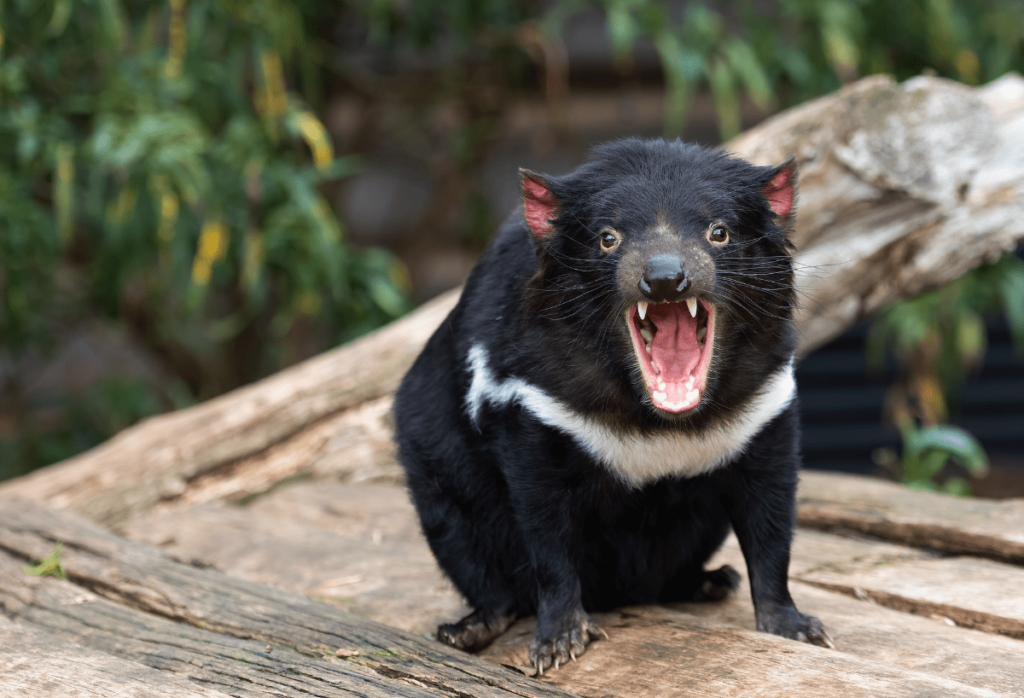

This carnivorous marsupial from Tasmania is mostly active at night. Tasmanian devils are scavengers and predators, known for their powerful jaws and ferocious feeding behavior. Their nocturnal habits help them avoid competition with diurnal predators and take advantage of the cover of darkness for hunting and scavenging.
Pangolins:
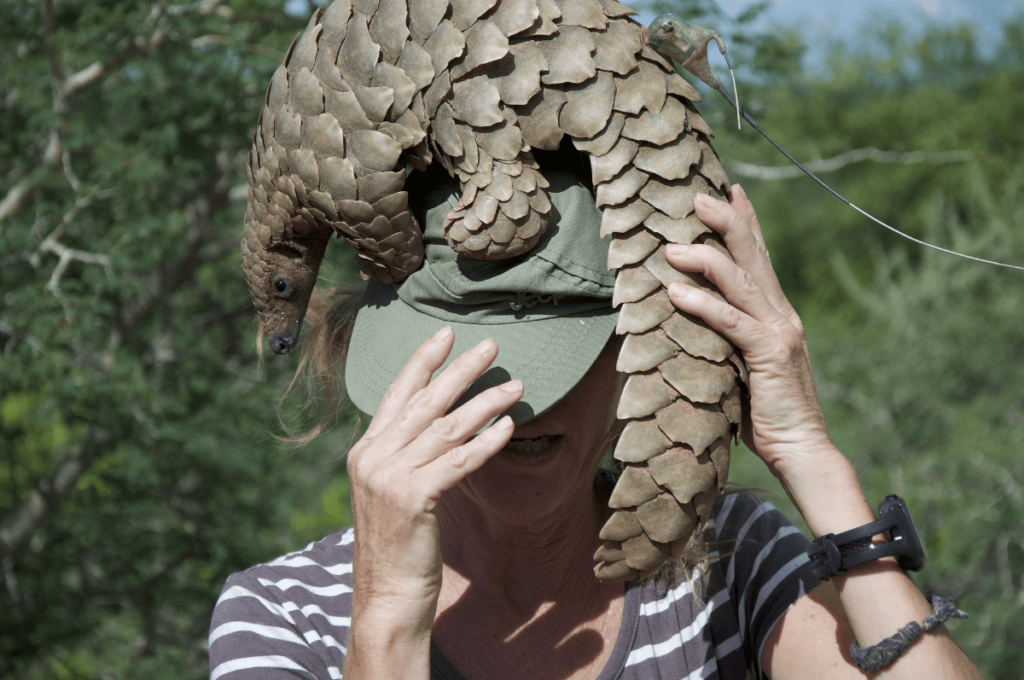

Pangolins, found in Africa and Asia, are nocturnal mammals covered in protective scales. They feed primarily on ants and termites, using their long, sticky tongue to extract insects from nests. Their nocturnal behavior helps them avoid daytime predators and take advantage of cooler temperatures for foraging.
Leopards:
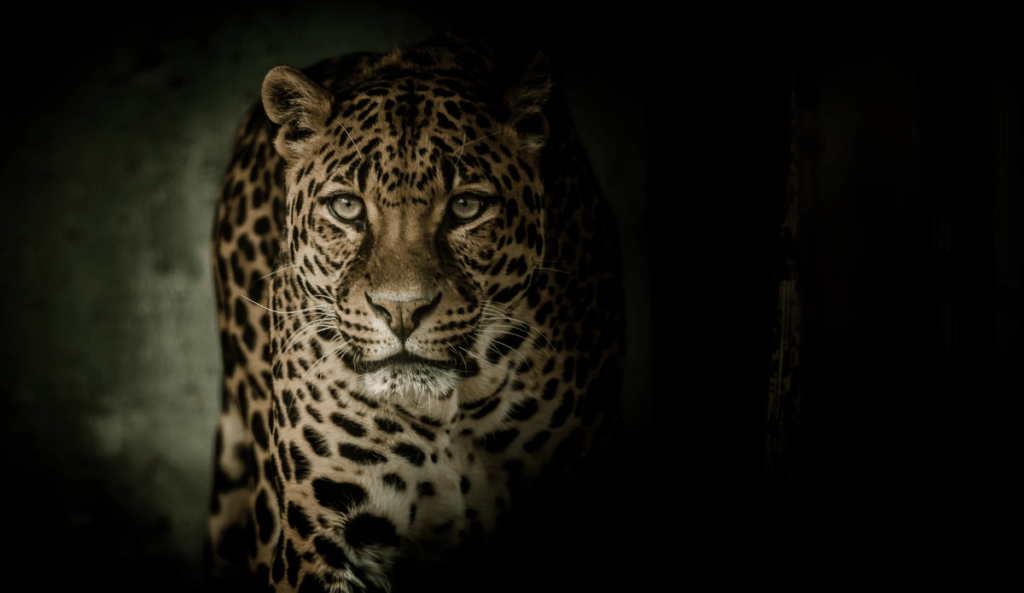

Leopards are elusive big cats that are primarily nocturnal predators. Their spotted coats provide camouflage in the dappled light of the forest floor, aiding their stealth as they stalk prey. Leopards are solitary hunters, using the cover of night to ambush and catch animals such as deer, boars, and smaller mammals.
For more insights into the impressive sizes of big cats, including the leopard and its larger relatives, check out our article on The Largest Cat Species in the World (Biggest Feline Species)
Birds
Owls:
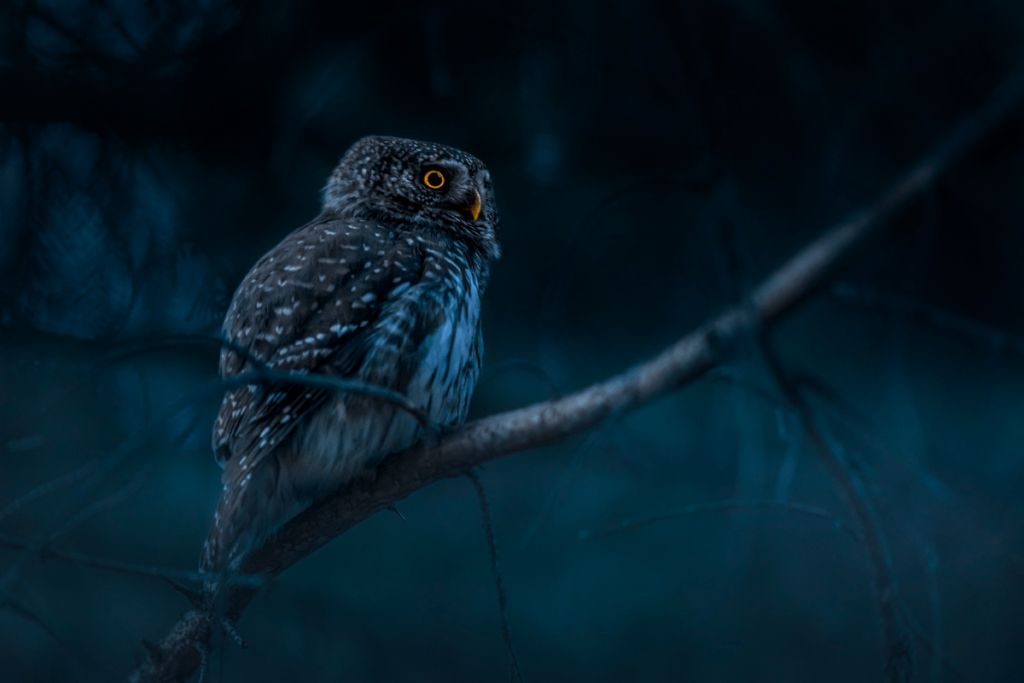

Owls, including species like the snowy owl and tawny owl, have evolved to be expert nocturnal hunters. Their exceptional night vision and silent flight enable them to hunt small mammals, insects, and other birds without being heard. Owls have specialized feathers that reduce flight noise, allowing them to swoop down on prey quietly.
Nightjars:
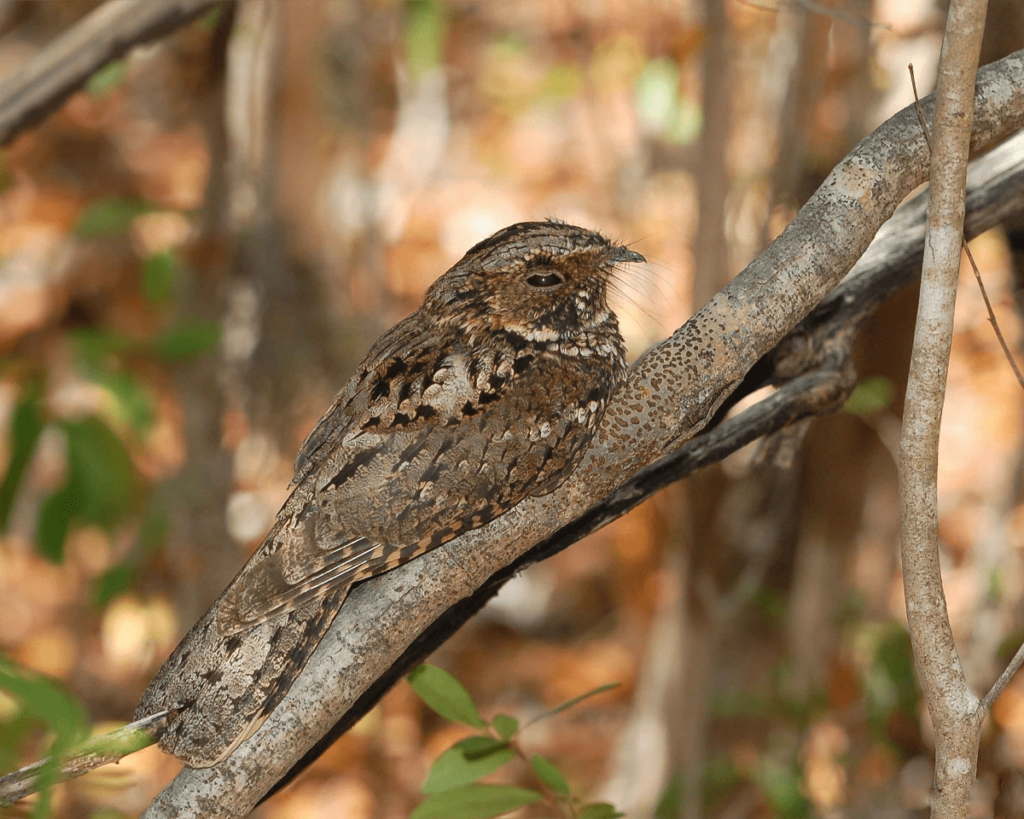

Nightjars are known for their cryptic plumage and nocturnal habits. Their mottled feathers blend with their surroundings, making them nearly invisible during the day. Nightjars feed on insects and use their silent flight to catch prey in mid-air. Their nocturnal behavior allows them to avoid predators and take advantage of nighttime insect activity.
Kiwi:
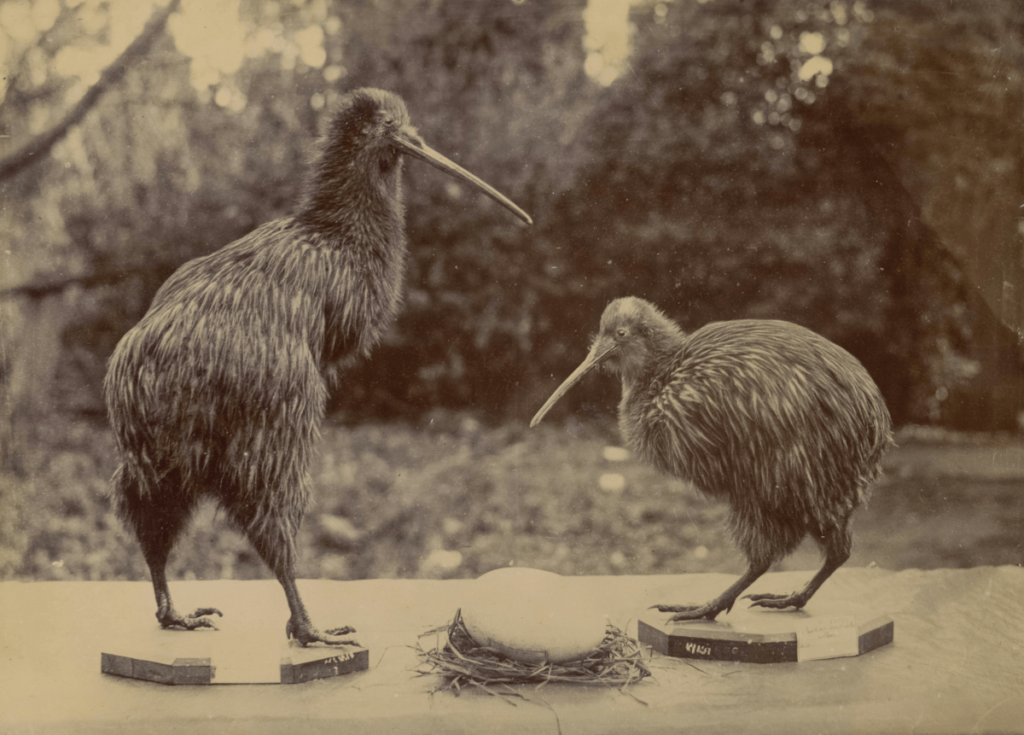

The kiwi is a flightless bird native to New Zealand, primarily nocturnal and adapted to foraging in the dark. Kiwis have highly sensitive nostrils at the tip of their beaks, which they use to probe the ground for insects and worms. Their nocturnal lifestyle helps them avoid predators and take advantage of the cooler nighttime temperatures.
Oilbird:
Found in South America, oilbirds are one of the few nocturnal fruit-eating birds. They use echolocation, similar to bats, to navigate through dark caves and forests where they roost and forage. Their nocturnal behavior helps them avoid predators and take advantage of fruit that ripens at night.
Frogmouths:
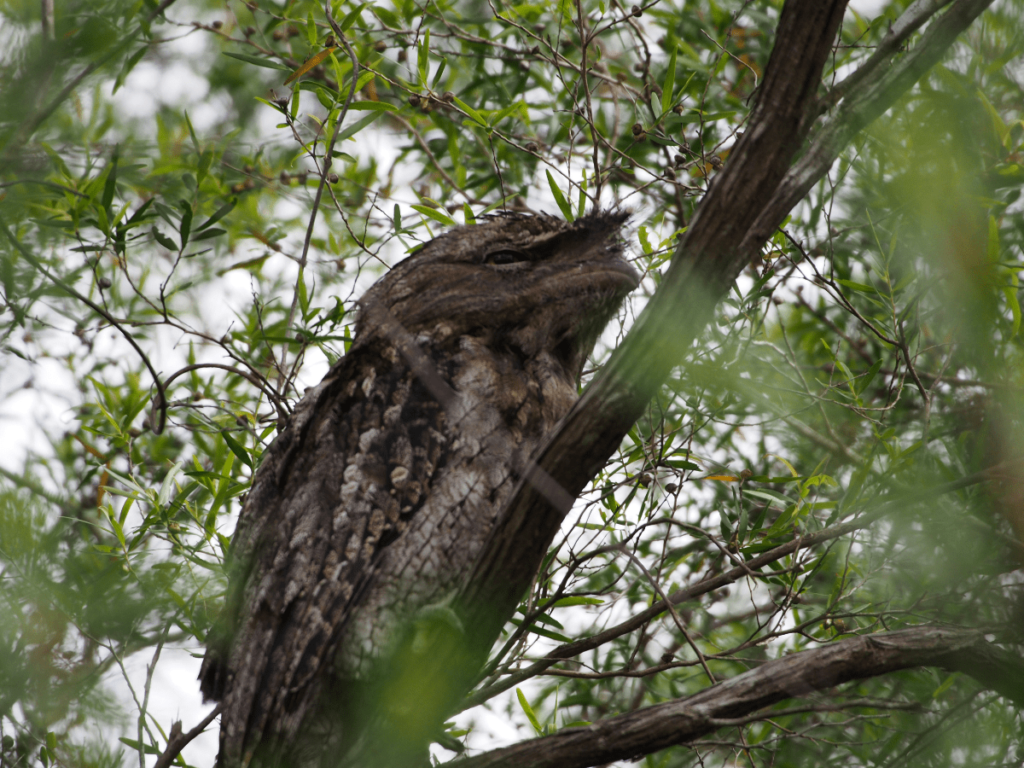

Frogmouths are nocturnal birds with large, frog-like mouths. They are known for their excellent camouflage, blending seamlessly with their surroundings during the day. Frogmouths feed on insects and small animals, using their wide mouths to catch prey in flight. Their nocturnal habits help them avoid predators and capitalize on nighttime insect activity.
Reptiles
Geckos:
Many geckos, including the leopard gecko, are nocturnal and use their large eyes to hunt insects in the dark. Their specialized toe pads allow them to climb vertical surfaces and hunt effectively at night. Geckos’ nocturnal behavior helps them avoid daytime predators and take advantage of the cooler nighttime foraging conditions.
Crested Gecko:
Native to New Caledonia, the crested gecko is a nocturnal reptile with unique appearance and behavior. It uses its adhesive toe pads to climb trees and hunt for insects and fruit at night. The crested gecko’s nocturnal lifestyle helps it avoid daytime predators and exploit nighttime food resources.
Ball Python:
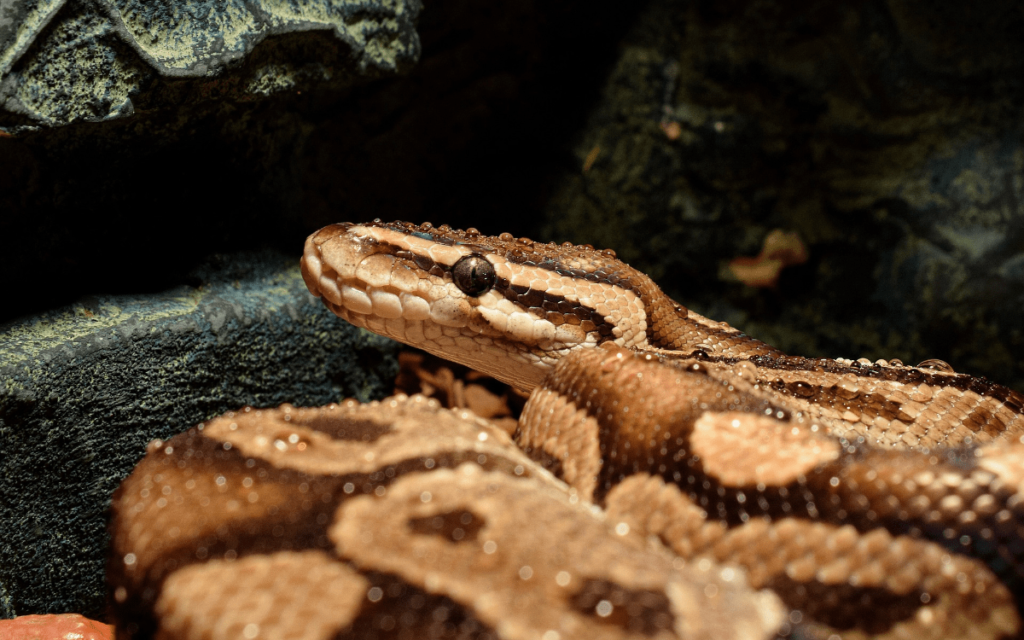

The ball python is a nocturnal snake from Africa known for its docile nature and defensive behavior of curling into a ball when threatened. As a nocturnal predator, it hunts small mammals and birds during the night. Its nocturnal habits help it avoid the heat of the day and competition with diurnal predators.
Caiman:
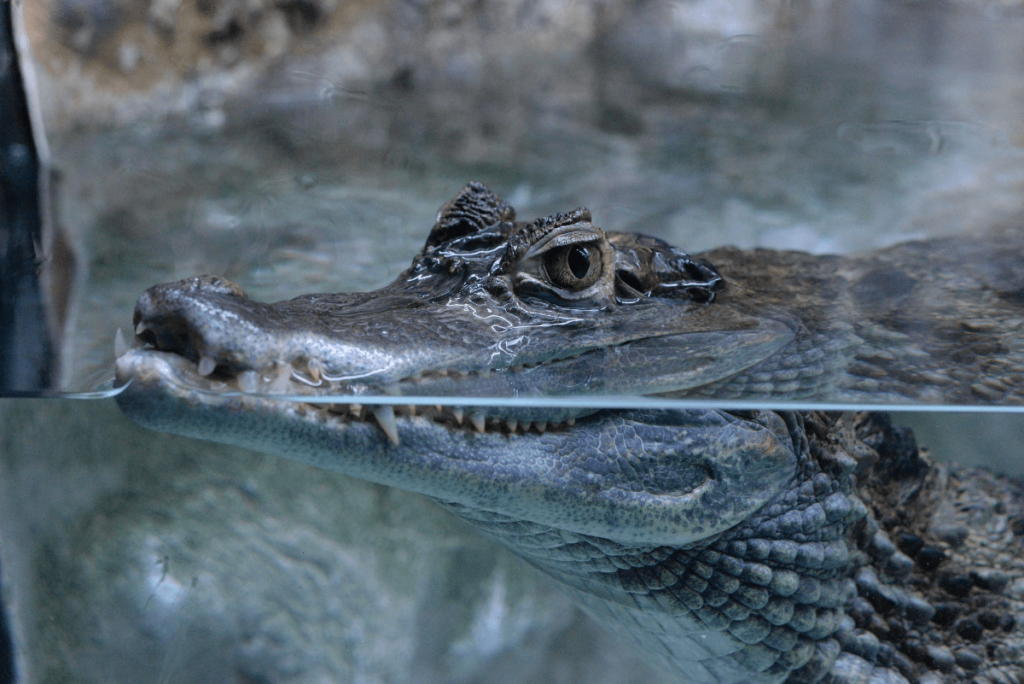

Caimans are small to medium-sized crocodilians that are primarily nocturnal. They hunt in the dark waters of Central and South America, using their keen sense of smell and night vision to ambush fish, birds, and small mammals. Their nocturnal activity helps them avoid daytime predators and competition with other predators.
Gila Monster:
The Gila monster is one of the few venomous lizards and is primarily nocturnal. It uses its venom for defense and relies on its slow-moving nature to avoid predators. The Gila monster’s nocturnal behavior helps it find food and avoid the heat of the day in its desert habitat.
Amphibians
Tree Frogs:
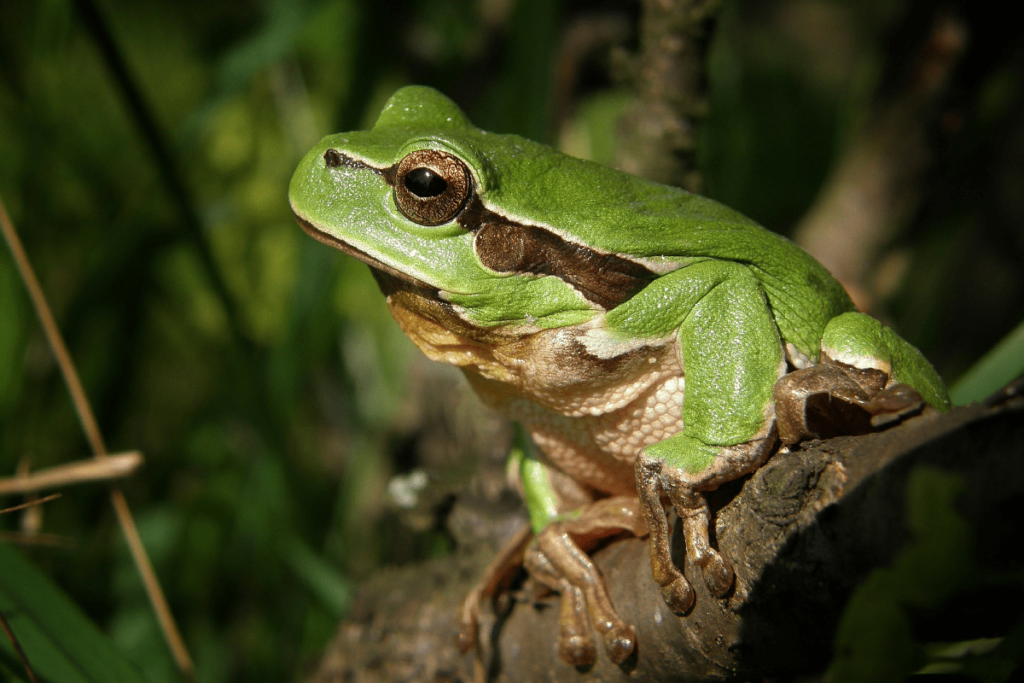

Tree frogs, including species like the red-eyed tree frog, are nocturnal amphibians that use their large eyes to hunt insects at night. They have webbed feet that allow them to climb trees and navigate their arboreal habitats. Their nocturnal habits help them avoid daytime predators and take advantage of nighttime insect activity.
Salamanders:
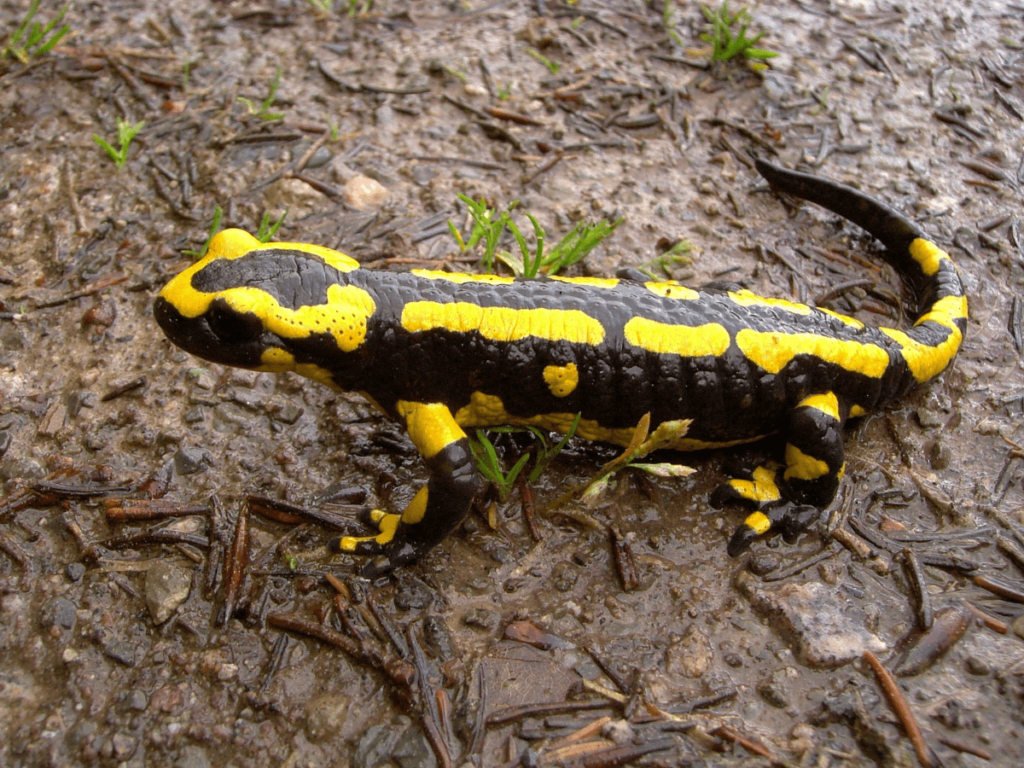

Salamanders, such as the spotted salamander, are nocturnal and often emerge after rainfall to hunt for invertebrates. Their moist skin is essential for respiration and helps them stay hydrated while foraging at night. Their nocturnal behavior allows them to avoid daytime predators and exploit nighttime food resources.
Newts:
Newts, including the Eastern newt, are nocturnal amphibians that hunt for small invertebrates during the night. Their life cycle includes aquatic larval stages and terrestrial adult stages, with nocturnal activity helping them avoid predators and take advantage of cooler nighttime temperatures.
Insects
Moths:
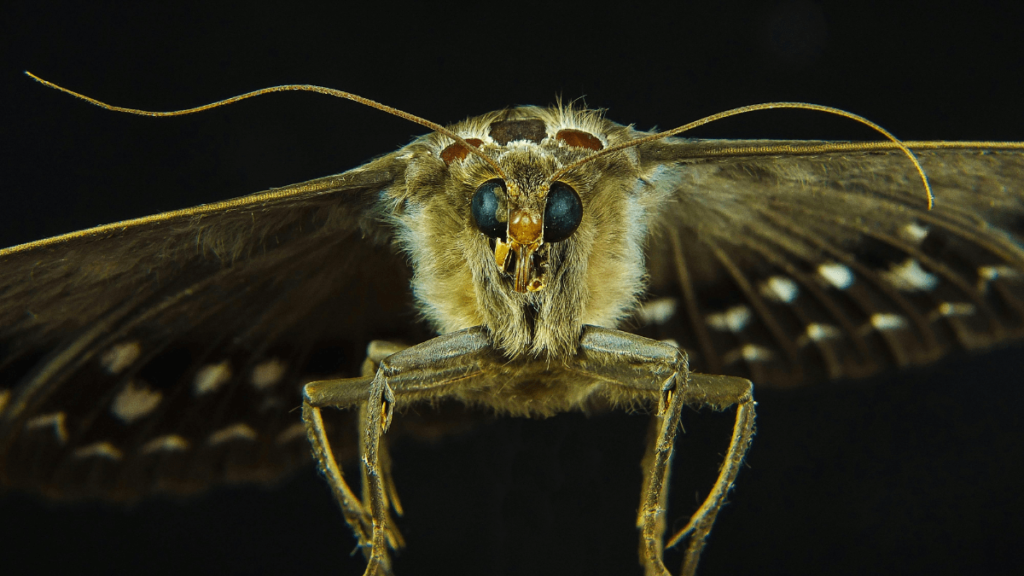

Moths, such as the Luna moth and Atlas moth, are nocturnal insects attracted to light sources. They have evolved to feed on nectar from night-blooming flowers and play a crucial role in pollination. Their nocturnal behavior helps them avoid daytime predators and capitalize on nighttime food resources.
Fireflies:
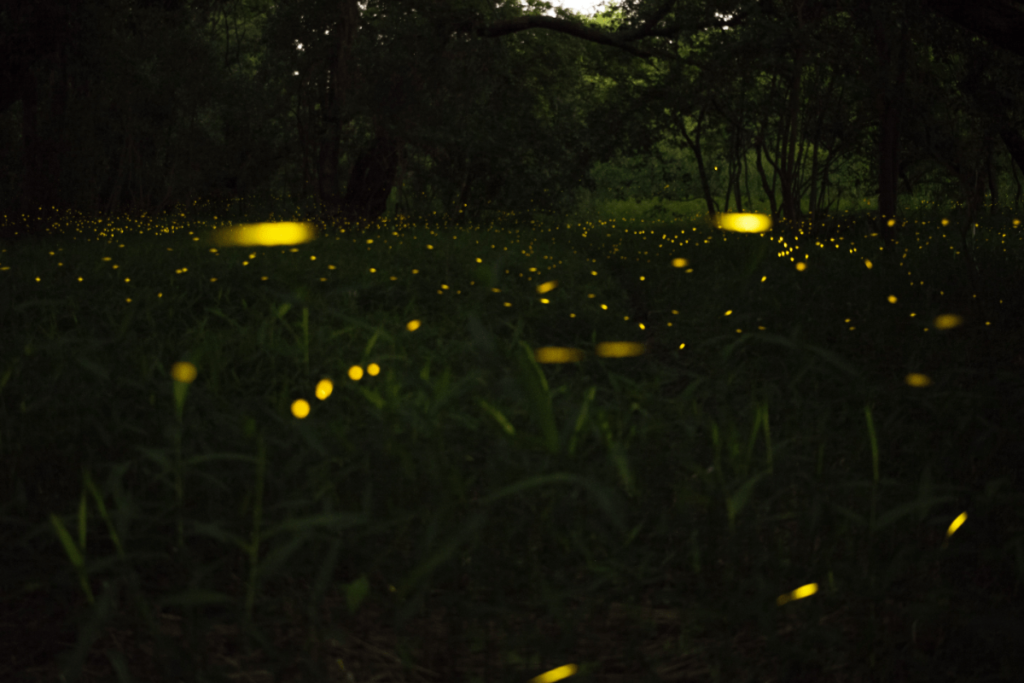

Fireflies are nocturnal insects known for their bioluminescent glow, which they use for mating and communication. Each species has a unique light pattern, making fireflies a captivating sight on warm summer nights. Their nocturnal habits help them avoid predators and attract mates through their glowing displays.
Cockroaches:
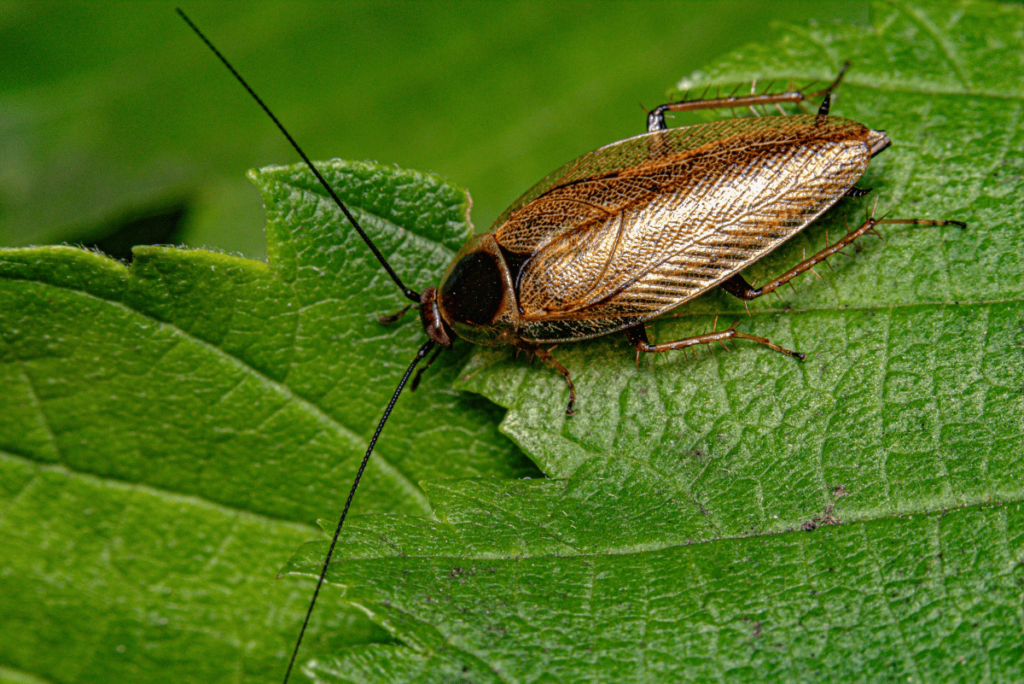

Cockroaches are nocturnal scavengers that feed on organic matter and decaying materials. Their nocturnal behavior helps them avoid human activity and predators while foraging for food. Cockroaches have adapted to survive in various environments, from urban areas to natural habitats.
Crickets:
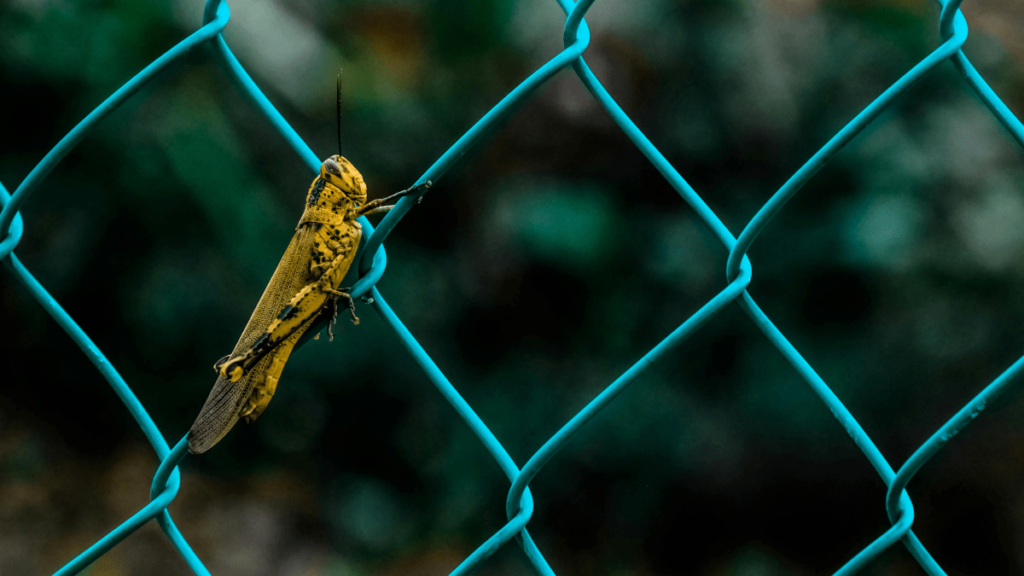

Crickets are known for their nocturnal chirping, which serves as a mating call. Their chirping is used by males to attract females and establish territory. Crickets’ nocturnal activity helps them avoid daytime predators and take advantage of nighttime mating opportunities.
Katydids:
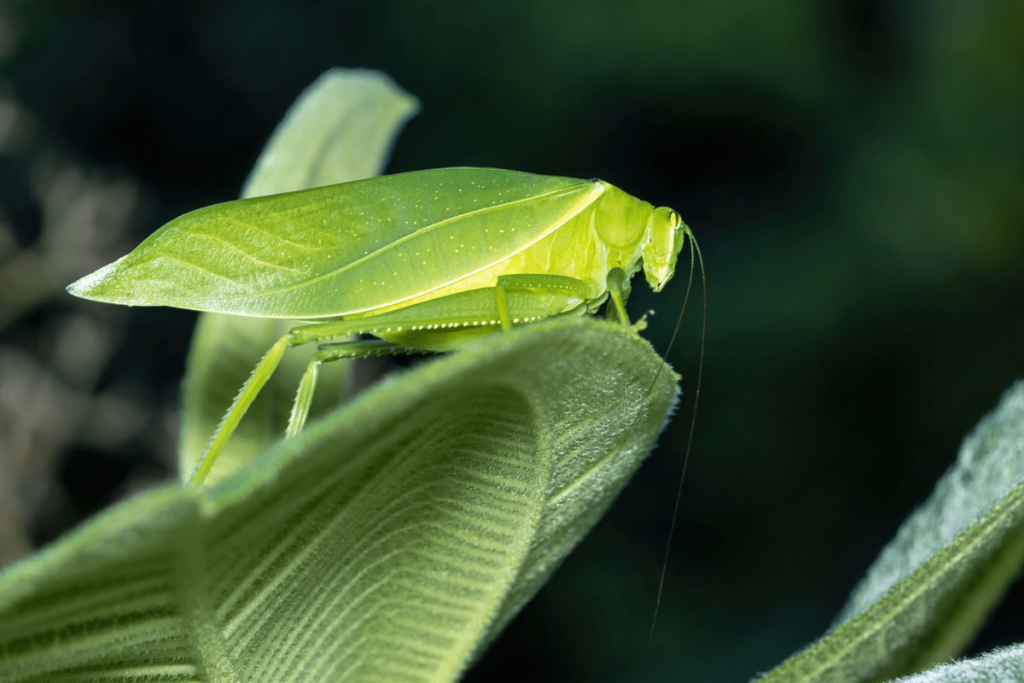

Katydids are insects known for their nocturnal songs, which are produced by rubbing their wings together. Their songs are used for communication and attracting mates. Katydids’ nocturnal behavior helps them avoid predators and take advantage of nighttime insect activity.
Fish & Marine Animals
Catfish:
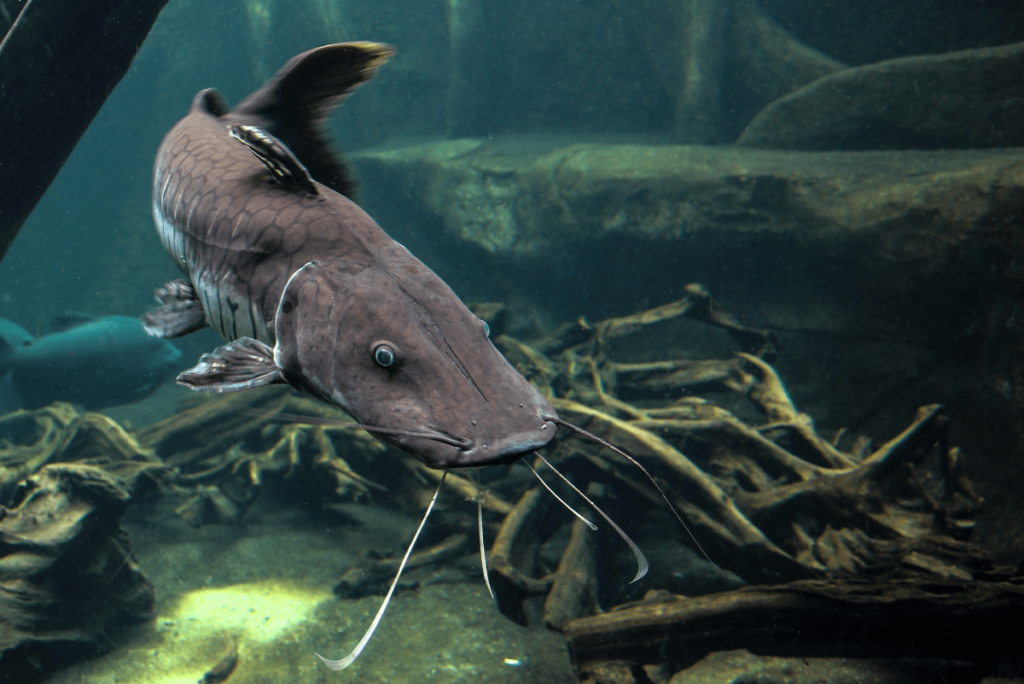
Catfish are nocturnal bottom feeders found in freshwater habitats worldwide. They use their barbels to detect food in the dark and are primarily active during the night. Their nocturnal behavior helps them avoid predators and find food in the murky waters where they live.
Sharks:
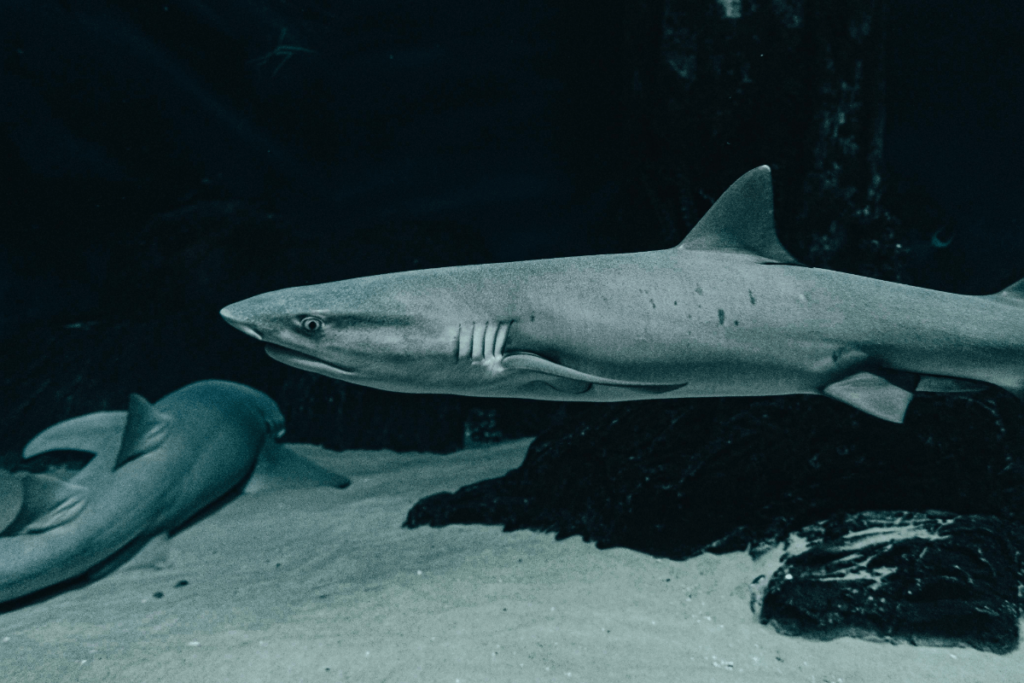

Some shark species, such as the nurse shark, are more active during the night. They use the cover of darkness to hunt for fish, crustaceans, and other prey. Their nocturnal habits help them avoid daytime predators and capitalize on the reduced visibility to ambush prey.
Sharks are among the longest-living animals; learn more in our article on The Longest Living Animals: Nature’s Oldest Survivors.
Octopus:
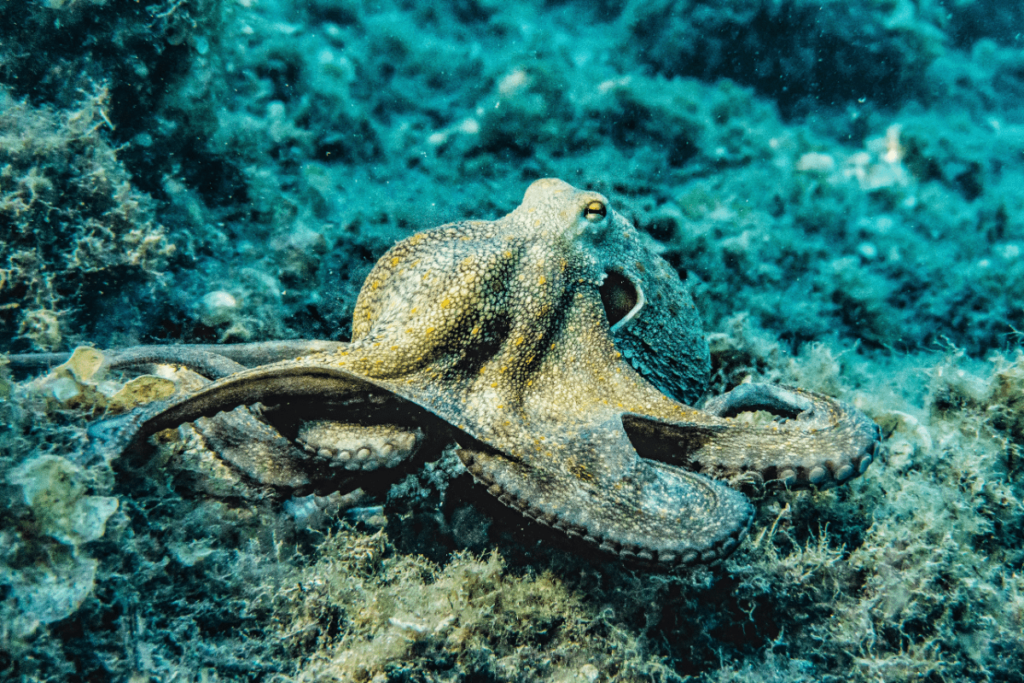

The common octopus is a nocturnal predator with exceptional camouflage abilities. It uses its intelligence and ability to change color and texture to blend with its surroundings while hunting at night. The nocturnal lifestyle helps the octopus avoid daytime predators and take advantage of nighttime prey.
To delve deeper into the remarkable cognitive abilities of the octopus and discover why it’s considered one of the most intelligent marine animals, check out our article How Smart Are Octopuses? 10 Fascinating Traits That Highlight Their Brainpower.
Moray Eels:
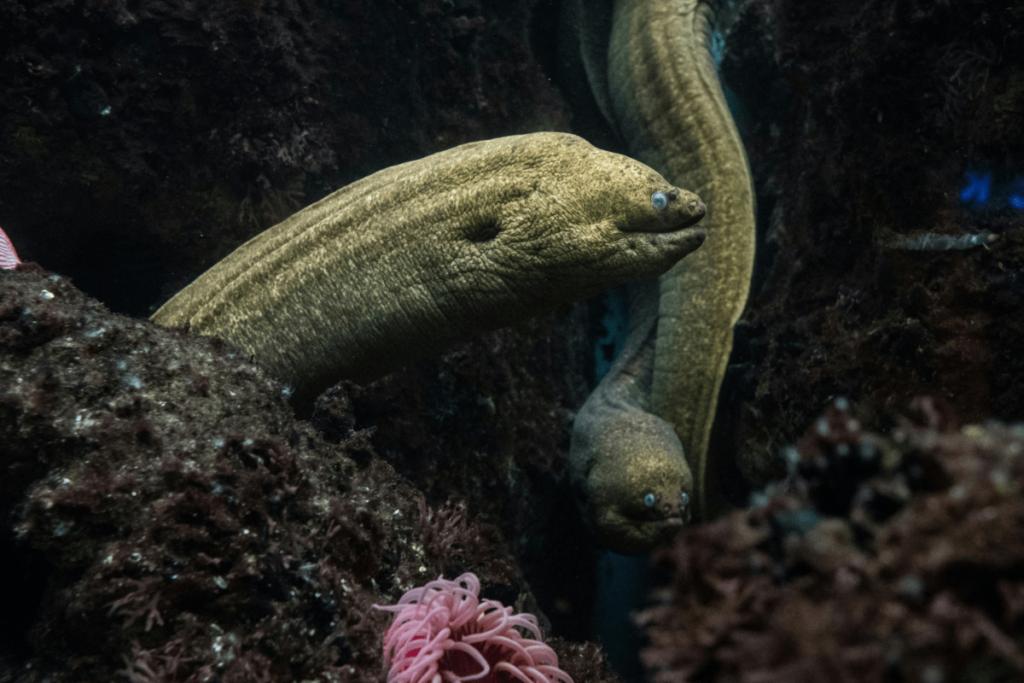

Moray eels are often more active during the night, hunting for fish and other prey in coral reefs. Their nocturnal behavior helps them avoid daytime predators and take advantage of the cover of darkness to ambush prey.
Other Nocturnal Animals
Scorpions:
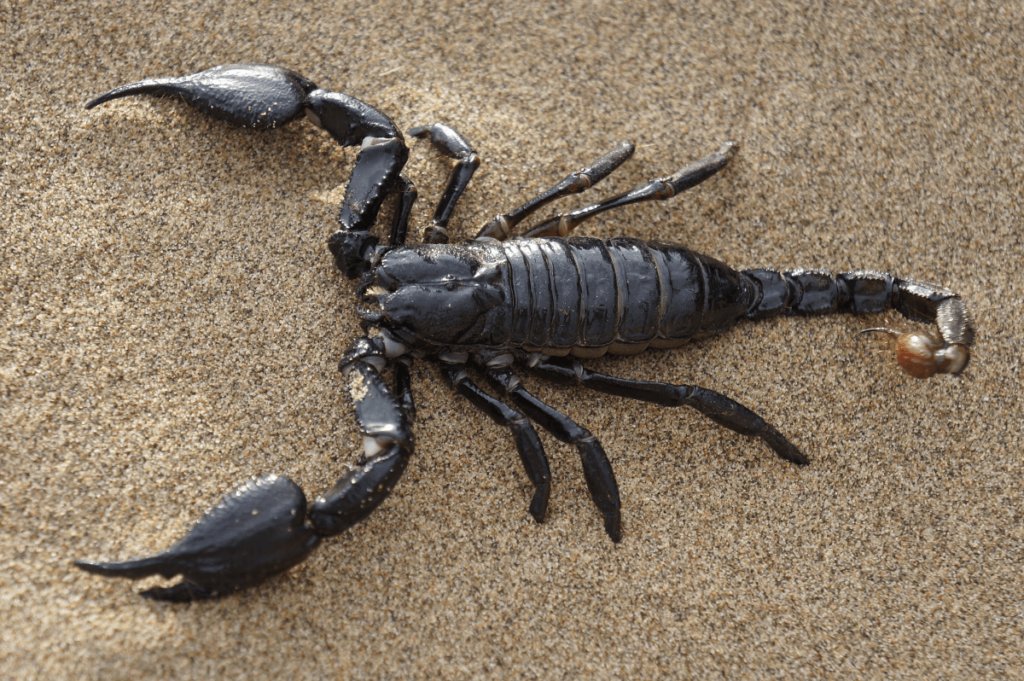

Scorpions are nocturnal predators found in deserts and tropical regions. They use their pincers and venomous stinger to capture and immobilize prey. Their nocturnal habits help them avoid daytime predators and hunt more effectively in the dark.
Tarantulas:
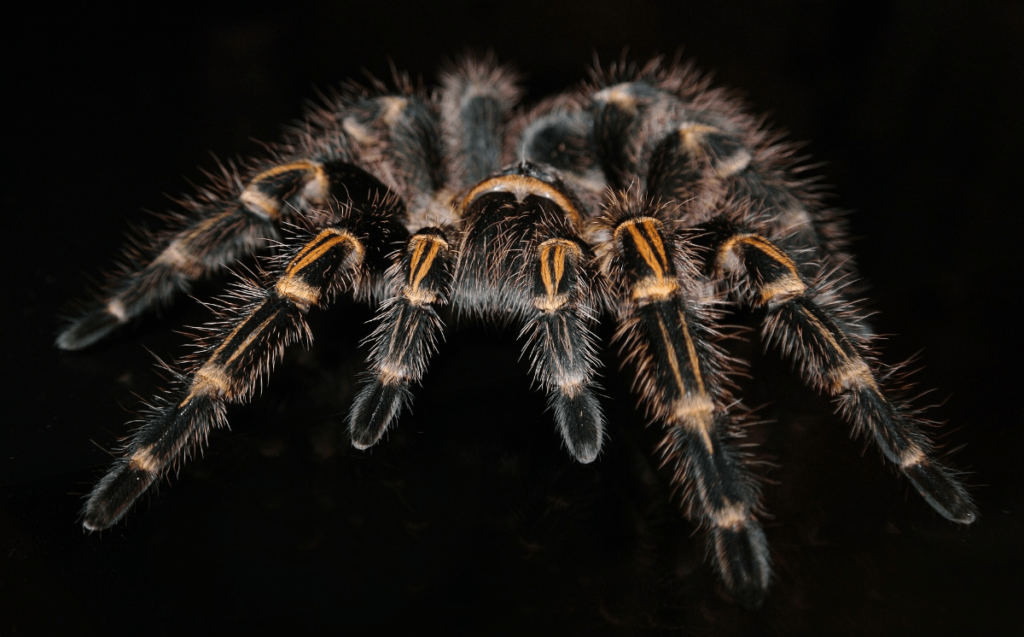

Tarantulas are large, nocturnal spiders that hunt for insects and small animals during the night. Their nocturnal behavior helps them avoid daytime predators and take advantage of the cooler nighttime temperatures for hunting.
Kangaroo Rat:
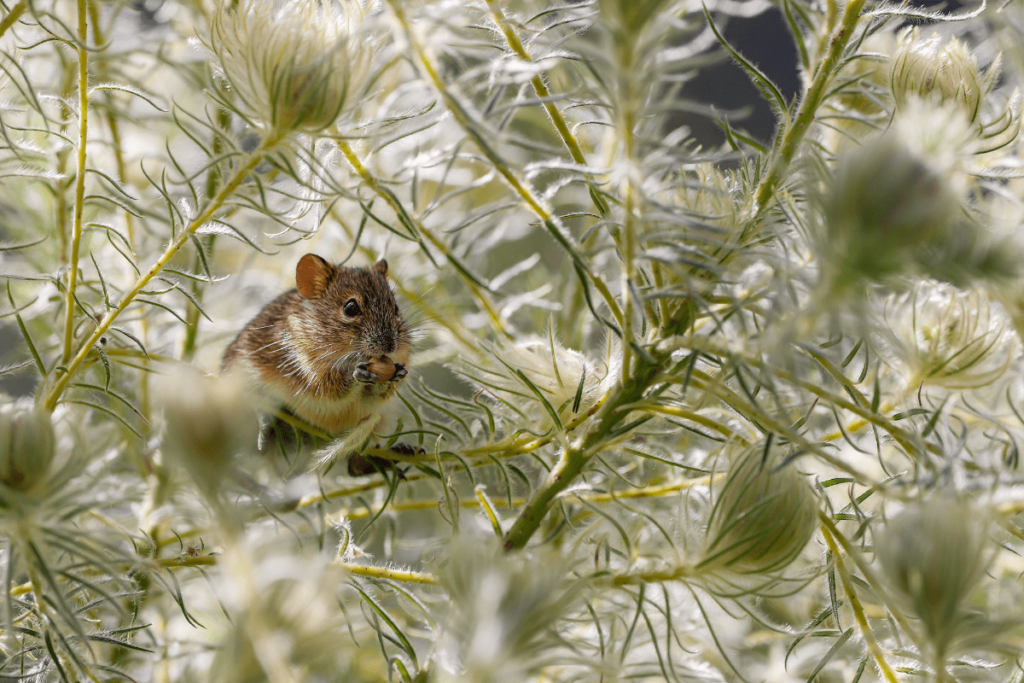

The kangaroo rat is a nocturnal rodent adapted to desert environments. It can survive without water by obtaining moisture from its food and using its nocturnal activity to avoid the extreme daytime temperatures of its habitat.
Wombat:
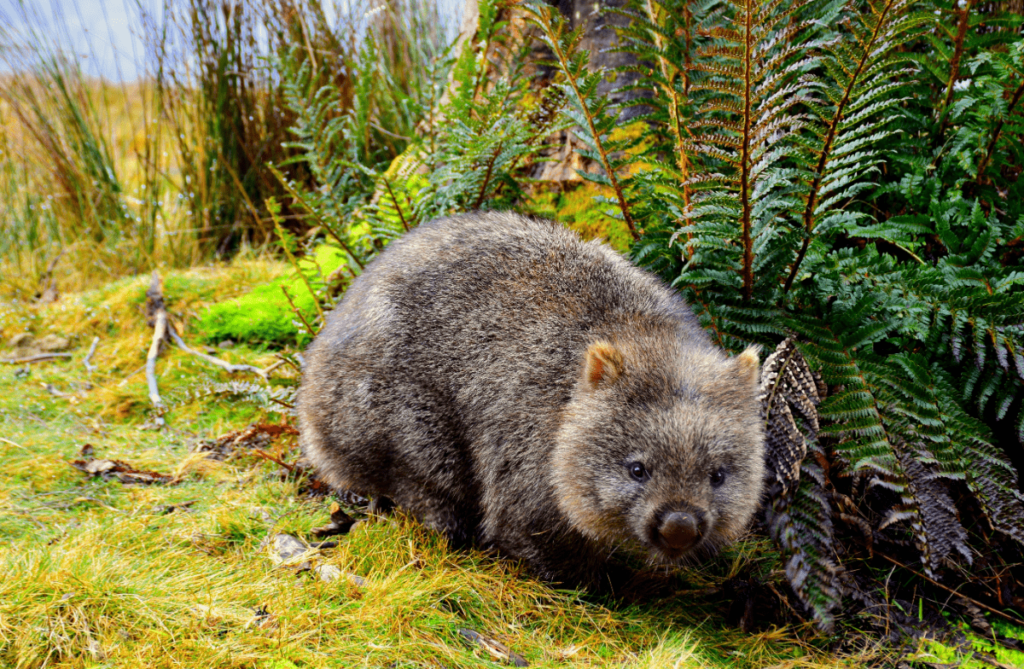

The wombat is a nocturnal marsupial native to Australia known for its burrowing habits. It forages for roots and grasses at night, avoiding daytime predators and taking advantage of the cooler temperatures for foraging.
Slow Loris:
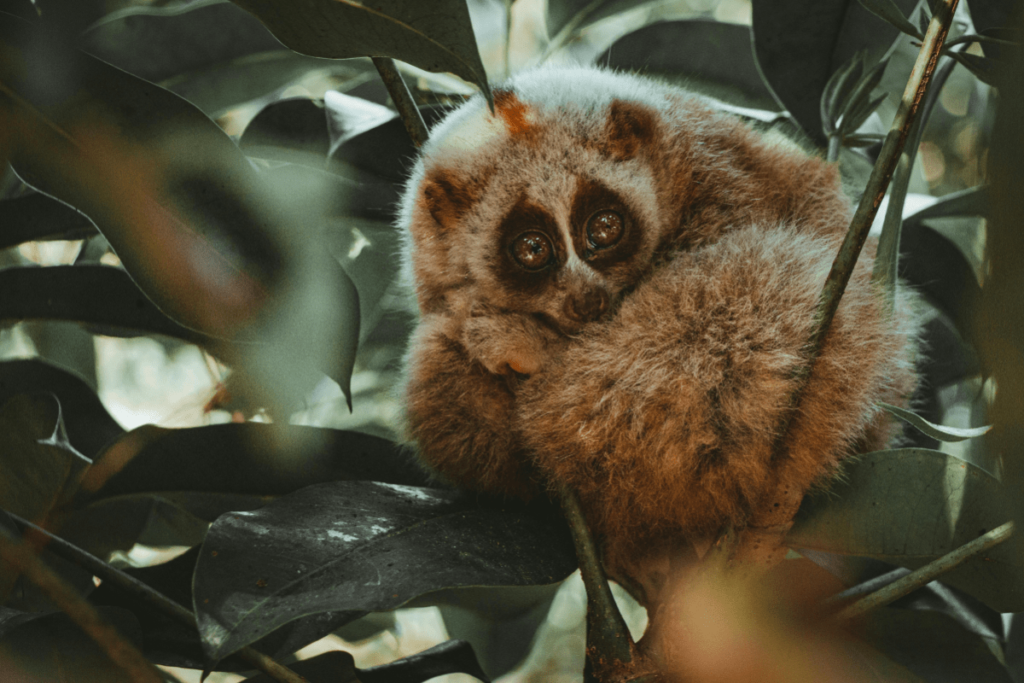

The slow loris is a nocturnal primate found in Southeast Asia. It is known for its slow movements and toxic bite, which it uses for defense. The slow loris’s nocturnal behavior helps it avoid daytime predators and exploit nighttime food resources.
Nighttime Animals vs. Nocturnal Animals
While all nocturnal animals are active at night, not all nighttime animals are strictly nocturnal. Nighttime animals may include species that are active during twilight hours or those that have irregular activity patterns.
They do not necessarily have the specialized adaptations seen in true nocturnal animals. Examples of nighttime animals include:
Deer:
While primarily crepuscular (active during dawn and dusk), some deer species are also active at night, especially in areas with human activity or where predators are prevalent.
Skunks:
Skunks are primarily nocturnal, but they might also be active during early evening or late morning hours, depending on their food sources and environmental pressures.
Rats:
Many species of rats exhibit nocturnal behavior, but they can also be seen at twilight or early morning if food resources are scarce or if they are disturbed.
The key difference lies in the consistency of their nocturnal behavior. True nocturnal animals are adapted specifically for life in the dark and exhibit consistent nighttime activity.
Nocturnal Animals in Different Habitats
Forest Nocturnal Animals
Forests provide a rich and diverse habitat for many nocturnal species. Animals like the slow loris and the aye-aye are examples of forest-dwelling nocturnal animals. These creatures have evolved to navigate the dense forest underbrush and canopy, using their senses and specialized limbs to move quietly and efficiently.
Examples include:
- Barred Owl
- Eastern Screech Owl
- Northern Long-Eared Bat
- African Bush Baby
- Greater Glider
Desert Nocturnal Animals
In the harsh desert environment, being nocturnal is often a matter of survival. The fennec fox, with its large ears that dissipate heat, and the kangaroo rat, which conserves water by producing highly concentrated urine, are prime examples of desert nocturnal animals. These species avoid the extreme daytime temperatures by being active during the cooler night hours.
Nocturnal animals in these habitats include:
- Fennec Fox
- Kangaroo Rat
- Gila Monster
- Night Stalker Scorpion
- Desert Toad
Urban Nocturnal Animals
As cities expand, many animals have adapted to urban environments, becoming nocturnal to avoid human activity. Raccoons, skunks, and opossums are common urban nocturnal animals that have learned to thrive in human-dominated landscapes. They often rely on human refuse for food and use urban structures for shelter.
Nocturnal animals that have adapted to city life include:
- Raccoons
- European Hedgehogs
- Peregrine Falcons
- Opossums
- Barn Owls
Impact of Human Activity on Nocturnal Animals
Human activity poses several challenges to nocturnal animals, with light pollution being one of the most significant. Artificial lights can disrupt the natural behaviors of nocturnal animals, affecting their hunting, mating, and navigation. Light pollution can disorient birds during migration and interfere with the reproductive cycles of nocturnal insects like fireflies.
Habitat destruction is another major threat. As forests, wetlands, and other natural habitats are cleared for agriculture or urban development, nocturnal animals lose their homes and food sources. This can lead to a decline in nocturnal species and disrupt the ecosystems they support.
Conservation Efforts for Nocturnal Animals
Efforts to conserve nocturnal animals often focus on habitat preservation and mitigating the impacts of light pollution. Protecting natural habitats, such as forests and wetlands, ensures that nocturnal animals have the space and resources they need to survive. Reducing light pollution, through measures like using lower-intensity lighting or shielding outdoor lights, can help maintain the natural behaviors of nocturnal species.
Some nocturnal animals are also part of targeted conservation programs. For example, the slow loris, a nocturnal primate from Southeast Asia, is protected under international law, with efforts to combat illegal wildlife trade and habitat loss.
Conclusion
Nocturnal animals play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems, acting as both predators and prey in the nighttime world. Their unique adaptations and behaviors allow them to thrive in environments where others might struggle. By understanding and protecting these fascinating creatures, we can ensure that the nighttime continues to be a thriving, vibrant part of the natural world. Next time you find yourself under the starry sky, take a moment to appreciate the hidden lives of nocturnal animals that make the night their own.




