What is animal conservation status?
Animal conservation status is a classification system used to assess the likelihood of a species becoming extinct. This system provides a clear picture of how close a species is to disappearing from the wild.
By evaluating factors such as population size, habitat quality, and threats, conservationists can determine the level of risk faced by each species. This classification is essential for guiding conservation efforts and ensuring that resources are allocated effectively to prevent species from becoming extinct.
Importance of understanding conservation status in protecting wildlife:
Understanding animal conservation status is crucial for prioritizing and directing conservation efforts. By knowing the conservation status of various species, we can identify those that are at the greatest risk and require immediate attention.
This information helps in implementing targeted actions to address specific threats, such as habitat destruction or illegal hunting. For instance, species classified as “Critically Endangered” require more urgent intervention compared to those categorized as “Near Threatened.”
Effective conservation strategies rely on this information to safeguard biodiversity and ensure the survival of at-risk species.

The Role of organizations like the IUCN:
Organizations such as the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) play a pivotal role in the assessment and categorization of species’ conservation status.
The IUCN Red List, developed by this organization, is a global authority on the conservation status of species. It provides a comprehensive and up-to-date inventory that classifies species into categories ranging from “Least Concern” to “Extinct.”
The information provided by the IUCN helps shape global conservation strategies and informs policymakers, researchers, and the public about the status of species and the urgency of their conservation needs.
The IUCN Red List
IUCN Red List (Global Authority on Conservation Status):
The IUCN Red List, maintained by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), is the foremost global inventory that assesses and monitors the conservation status of species.
This comprehensive database provides crucial information on the risk of extinction faced by species around the world. The IUCN Red List serves as a critical tool for scientists, conservationists, and policymakers, offering an up-to-date overview of the health of global biodiversity.
By categorizing species based on their risk of extinction, the Red List helps prioritize conservation efforts and supports informed decision-making to protect endangered and threatened species.
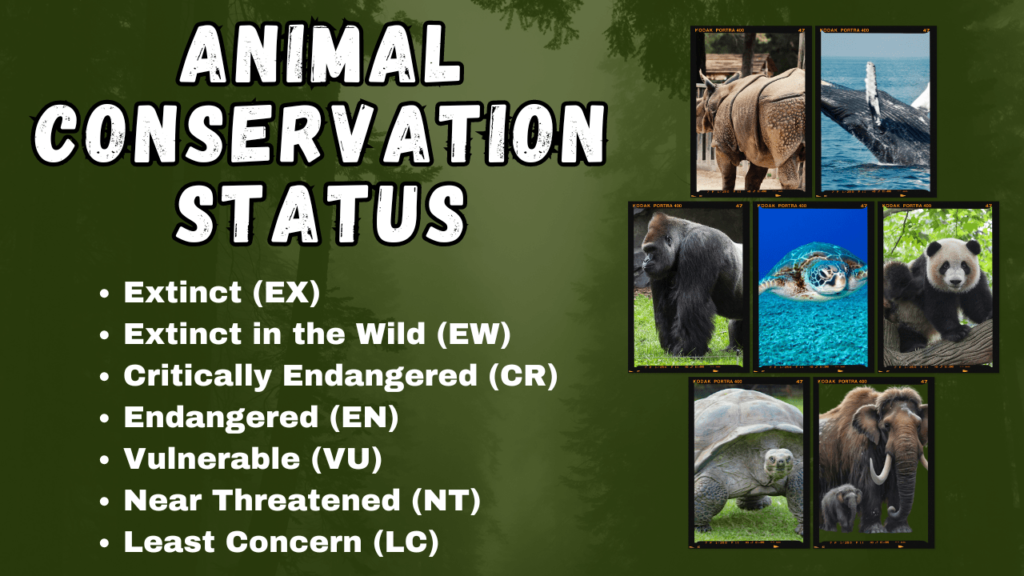
Categories and what they mean:
1.Extinct (EX):
Species classified as “Extinct” have no known surviving individuals anywhere in the world. This category is used for species that have completely disappeared, with no living members found in their natural habitats or in captivity.
Examples: Passenger Pigeon, Pinta Island Tortoise, Barbary Lion, Splendid Poison Frog, Yangtze Giant Softshell Turtle
You can check out the List of 20 Notable Extinct Animals and the Shocking Reasons Behind Their Extinction

2.Extinct in the Wild (EW):
Species listed as “Extinct in the Wild” are known only from individuals that live in captivity or in locations outside their natural range.
These species no longer exist in their original habitats, which means that any remaining individuals are only found in controlled environments such as zoos, aquariums, or botanical gardens.
Examples: California Condor, Mauritius Kestrel, Lord Howe Island Phasmid, Scalesia pedunculata, Guam Kingfisher

3.Critically Endangered (CR):
The “Critically Endangered” category (also called as Near Extinct) denotes species that face an extremely high risk of extinction in the wild. This designation is given to species that are on the brink of disappearing and are often facing severe threats from habitat loss, poaching, or environmental changes.
Immediate and intensive conservation efforts are required to prevent their extinction.
Examples: Vaquita, Saola, Javan Rhino, Sumatran Orangutan, Amur Leopard
Here is a list of 20 Critically Endangered Species Fighting for Survival

4.Endangered (EN):
Species categorized as “Endangered” are at a high risk of extinction in the wild. They are experiencing significant declines in population and are threatened by factors such as habitat destruction, overexploitation, or climate change.
Although not as dire as “Critically Endangered,” these species still require substantial conservation actions to improve their status and prevent further decline.
Examples: Sumatran Tiger, Asian Elephant, Hawksbill Turtle, Mountain Gorilla, Northern Bald Ibis
Here is a list of The 15 Most Endangered Species

5.Vulnerable (VU):
The “Vulnerable” category is used for species that are at high risk of becoming endangered in the wild in the near future. These species are currently experiencing threats that could lead to more severe declines if conditions do not improve.
Conservation efforts are necessary to address the factors contributing to their vulnerability and to stabilize or increase their populations.
Examples: African Elephant, Snow Leopard, Kakapo, Giant Panda, Bongo Antelope

6.Near Threatened (NT):
Species classified as “Near Threatened” are at risk of becoming endangered in the near future. Although they are not currently considered threatened, they are facing pressures that could lead to their decline if these pressures continue or intensify.
Monitoring and proactive conservation measures are needed to prevent these species from moving into a higher risk category.
Examples: Green Sea Turtle, Greater Flamingo, Indian Star Tortoise, Narwhal, Red-crowned Crane

7.Least Concern (LC):
The “Least Concern” category is used for species that are currently considered to be at low risk of extinction in the wild.
These species are widespread and abundant, facing no immediate threat of significant population decline or habitat loss. Their populations are stable or increasing, and they do not currently meet the criteria for any higher risk categories.
Although these species are not currently at risk, continuous monitoring and conservation efforts are important to ensure that their status remains stable and to address any emerging threats.
Examples: American Bison, Gray Wolf, Fennec Fox, Bald Eagle, African Buffalo, Golden Eagle, Green Sea Turtle, Honey Badger, Mountain Gorilla, Platypus, Snow Leopard, Nile Crocodile, Humpback Whale, Green Sea Turtle

Importance of Biodiversity
Role of Biodiversity:
- Maintaining Healthy Ecosystems: Biodiversity, which refers to the variety of life forms within a given ecosystem, plays a crucial role in ecosystem stability and resilience. A diverse range of species contributes to various ecological functions such as nutrient cycling, pollination, and soil fertility. Biodiversity conservation ensures that these vital processes continue, supporting ecosystem health and productivity.
- Ecosystem Services: Diverse ecosystems provide essential services such as clean air and water, climate regulation, and disease control. By preserving biodiversity, we help maintain these services that are critical for human survival and well-being.
Impact of Species Loss:
- Disruption of Ecological Balance: The extinction or decline of one species can lead to cascading effects throughout the ecosystem. For example, the loss of a predator can result in overpopulation of prey species, which may then overconsume vegetation, leading to habitat degradation.
- Altered Ecosystem Functions: The absence of certain species can disrupt ecological processes. For instance, the loss of pollinators like bees can affect plant reproduction and lead to declines in plant populations, which in turn impacts other species that depend on those plants for food or habitat.
- Decreased Resilience: Ecosystems with high biodiversity are better able to withstand and recover from environmental changes and disturbances. When biodiversity is lost, ecosystems become more fragile and less capable of adapting to changes such as climate shifts or natural disasters.

Factors Contributing to Species Decline
Human Activities:
Habitat Destruction: This occurs primarily due to deforestation, urbanization, and agricultural expansion. When forests are cleared for agriculture or urban development, many species lose their natural habitats, leading to decreased populations and increased risk of extinction.

Pollution: Pollutants from industrial activities, agricultural runoff, and improper waste disposal contaminate air, water, and soil. This pollution can lead to habitat degradation, reduced food availability, and health problems for wildlife, making it harder for species to survive.

Illegal Hunting: Poaching and illegal wildlife trade target animals for their body parts, such as ivory, fur, and bones. This not only reduces population numbers but can also disrupt ecological balances as keystone species are removed from their habitats.

Impact on Species:
- Reduced Food Sources: As habitats are destroyed or polluted, the availability of food resources decreases. Species that rely on specific plants or animals may struggle to find adequate nutrition, leading to malnutrition and population declines.
- Habitat Loss: The destruction of natural habitats forces species into smaller and often fragmented areas. This can lead to overcrowding, competition for resources, and increased vulnerability to predators and environmental changes.
- Increased Vulnerability: The combined effects of habitat loss, pollution, and illegal hunting make species more susceptible to diseases, extreme weather events, and other environmental stressors. This heightened vulnerability further exacerbates their risk of decline and extinction.

Conservation Efforts
Overview of Global Conservation Efforts:
Global conservation efforts are vital in protecting endangered species and preserving biodiversity. These efforts encompass various strategies and initiatives designed to address the numerous threats faced by wildlife.
Check out Conservation Status of Pandas
- Creating Protected Areas: Establishing national parks, wildlife reserves, and marine protected areas helps safeguard critical habitats from human activities. These areas provide refuge for species to thrive and recover without the pressures of habitat destruction and exploitation.
- Enforcing Wildlife Laws: Strengthening and enforcing legal protections against poaching, illegal trade, and habitat destruction is crucial. Laws and regulations, such as bans on hunting and trading endangered species, help reduce human impact on wildlife.
- Conducting Research: Scientific research plays a key role in informing conservation strategies. By studying species’ behaviors, populations, and habitats, researchers can develop targeted interventions and measure the effectiveness of conservation actions.

Examples of Successful Recovery Programs:
The Giant Panda and Bald Eagle are great examples of Successful Conservation Efforts.
Check out this article: Endangered Species Status Changes.
Programs:
- Protected Areas: National parks, wildlife reserves, and marine protected areas serve as sanctuaries where wildlife can live and reproduce without the immediate threats of human activities. Examples include the Serengeti National Park in Tanzania and the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park in Australia.
- Wildlife Corridors: These are designated pathways that connect protected areas, allowing animals to migrate, find food, and breed. Corridors help maintain genetic diversity and prevent inbreeding. For instance, the Yellowstone to Yukon Conservation Initiative provides a corridor for wildlife across North America’s Rocky Mountains.
- Breeding Programs: Captive breeding and reintroduction programs are essential for increasing the populations of critically endangered species. Programs for species like the California Condor and the Black-footed Ferret have successfully reintroduced individuals into their natural habitats, aiding in their recovery and survival.

How Individuals Can Help
Support Conservation Organizations:
- Contribute Financially: Donations to organizations focused on wildlife conservation, such as the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), the Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS), and the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), help fund essential projects and research. Financial support is crucial for maintaining protected areas, conducting field research, and implementing conservation strategies.
- Volunteer: Many organizations offer volunteer opportunities, from participating in local conservation projects to helping with administrative tasks. Volunteering can provide valuable hands-on experience and help advance conservation goals. Examples include joining clean-up efforts, assisting with wildlife monitoring, or working with community education programs.
Reduce Your Environmental Footprint:
- Adopt Eco-Friendly Practices: Make conscious choices to reduce your environmental impact. This includes minimizing waste by recycling and composting, conserving energy by using energy-efficient appliances, and reducing water consumption.
- Support Sustainable Products: Opt for products that are environmentally friendly and sustainably sourced. This can include choosing products with eco-friendly packaging, supporting companies with strong environmental policies, and avoiding items that contribute to habitat destruction, such as those linked to deforestation.
Spread Awareness and Advocacy:
- Share Information: Use social media platforms, blogs, and community events to spread knowledge about wildlife conservation issues. Sharing informative content can help raise awareness and encourage others to take action.
- Participate in Community Efforts: Engage in or organize local conservation initiatives, such as tree planting events, wildlife monitoring programs, or educational workshops. Community involvement helps create a culture of conservation and can lead to meaningful local impact.
- Advocate for Policies: Support and advocate for environmental policies and legislation that protect wildlife and natural habitats. This includes participating in campaigns, contacting policymakers, and supporting organizations that lobby for stronger conservation laws and protections.
By taking these actions, individuals can make a significant difference in the effort to protect endangered species and promote a healthier planet. Every small action contributes to the broader goal of wildlife conservation and sustainability.

Conclusion
Understanding conservation status is crucial for effectively addressing the challenges faced by endangered species. By classifying species based on their risk of extinction, we can prioritize conservation efforts, allocate resources more efficiently, and implement targeted actions to protect those most at risk.
This knowledge helps guide decision-making processes and informs the development of strategies to prevent species from disappearing.
As individuals, we all have a role to play in the conservation of wildlife.
Here’s how you can contribute:
- Support Conservation Efforts: Contribute to or volunteer with organizations dedicated to protecting endangered species. Your support helps fund critical conservation projects and ensures that efforts to safeguard wildlife continue.
- Adopt Sustainable Practices: Make environmentally conscious choices in your daily life. Reducing waste, conserving energy, and supporting sustainable products are steps that can reduce your environmental footprint and support broader conservation goals.
- Spread Awareness: Share information about conservation issues with your community and network. By raising awareness and advocating for wildlife protection, you help build a collective effort to address the challenges facing endangered species.
Together, we can make a significant impact on the preservation of our planet’s biodiversity.
Take action today to support conservation efforts and contribute to the protection and recovery of endangered species.
Your involvement matters and can help ensure a brighter future for wildlife around the world.
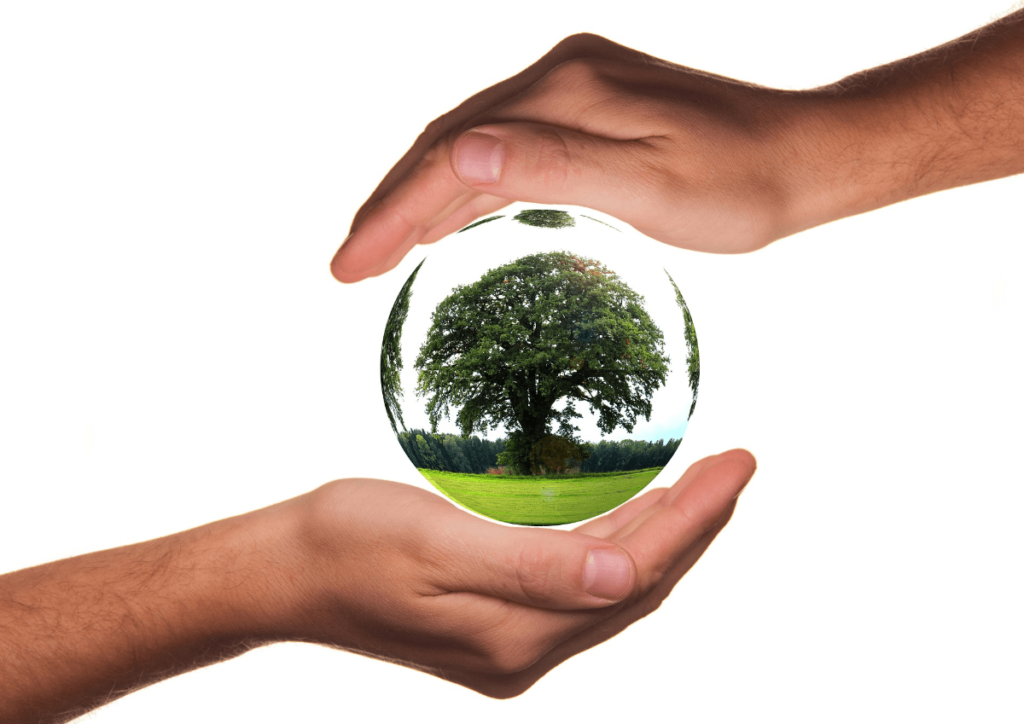

Animal Conservation Status (2024-2025):
| Animal | Conservation Status | Approximate Number |
|---|---|---|
| lion conservation status | Vulnerable (VU) | 20,000 |
| tiger conservation status | Endangered (EN) | 3,900 |
| cheetah conservation status | Vulnerable (VU) | 7,100 |
| red panda conservation status | Endangered (EN) | 1,500 |
| sumatran tiger conservation status | Critically Endangered (CR) | 400 |
| capybara conservation status | Least Concern (LC) | 1,000,000+ |
| polar bear conservation status | Vulnerable (VU) | 22,000 |
| black rhinoceros conservation status | Critically Endangered (CR) | 5,000 |
| jaguar conservation status | Near Threatened (NT) | 15,000 |
| orca conservation status | Data Deficient (DD) | 50,000+ |
| bald eagle conservation status | Least Concern (LC) | 40,000+ |
| cape buffalo conservation status | Least Concern (LC) | 400,000+ |
| african buffalo conservation status | Least Concern (LC) | 900,000+ |
| african lion conservation status | Vulnerable (VU) | 23,000 |
| conservation status of lions | Vulnerable (VU) | 23,000 |
| conservation status of orcas | Data Deficient (DD) | 50,000+ |
| conservation status of pandas | Vulnerable (VU) | 1,500 |
| giant panda conservation status | Vulnerable (VU) | 1,500 |
| great white shark conservation status | Vulnerable (VU) | 3,500 |
| manatee conservation status | Vulnerable (VU) | 13,000 |
| orca whale conservation status | Data Deficient (DD) | 50,000+ |
| panda conservation status | Vulnerable (VU) | 1,500 |
| siberian tiger conservation status | Endangered (EN) | 500 |
| vaquita conservation status | Critically Endangered (CR) | 10 |
| asiatic cheetah conservation status | Critically Endangered (CR) | 50 |
| bengal tiger conservation status | Endangered (EN) | 2,500 |
| blue whale conservation status | Endangered (EN) | 10,000+ |
| conservation status of giant panda | Vulnerable (VU) | 1,500 |
| cougar conservation status | Least Concern (LC) | 50,000+ |
| killer whale conservation status | Data Deficient (DD) | 50,000+ |
| lear’s macaw conservation status | Critically Endangered (CR) | 200 |
| snow leopard conservation status | Vulnerable (VU) | 4,000 |
| amur tiger conservation status | Endangered (EN) | 500 |
| arctic fox conservation status | Least Concern (LC) | 300,000+ |
| conservation status of great white shark | Vulnerable (VU) | 3,500 |
| fennec fox conservation status | Least Concern (LC) | 250,000+ |
| giraffe conservation status | Vulnerable (VU) | 68,000 |
| gray wolf conservation status | Least Concern (LC) | 200,000+ |
| grey wolf conservation status | Least Concern (LC) | 200,000+ |
| grizzly bear conservation status | Least Concern (LC) | 55,000 |
| hippopotamus conservation status | Vulnerable (VU) | 115,000 |
| humpback whale conservation status | Least Concern (LC) | 80,000+ |
| quokka conservation status | Vulnerable (VU) | 8,000 |
| white rhinoceros conservation status | Critically Endangered (CR) | 18,000 |
| wolf conservation status | Least Concern (LC) | 200,000+ |
| bobcat conservation status | Least Concern (LC) | 1,000,000+ |
| chimpanzee conservation status | Endangered (EN) | 300,000 |
| coyote conservation status | Least Concern (LC) | 500,000+ |
| elephant conservation status | Vulnerable (VU) | 415,000 |
| european bison conservation status | Near Threatened (NT) | 4,000 |
| golden eagle conservation status | Least Concern (LC) | 80,000+ |
| iucn conservation status | (General Term) | – |
| ocelot conservation status | Least Concern (LC) | 40,000+ |
| orangutan conservation status | Critically Endangered (CR) | 55,000 |
| rhino conservation status | Critically Endangered (CR) | 27,000 |
| rhinoceros conservation status | Critically Endangered (CR) | 27,000 |
| black bear conservation status | Least Concern (LC) | 900,000+ |
| hammerhead shark conservation status | Vulnerable (VU) | 200,000+ |
| mountain gorilla conservation status | Critically Endangered (CR) | 1,000 |
| peacock mantis shrimp conservation status | Least Concern (LC) | 200,000+ |
| platypus conservation status | Near Threatened (NT) | 2,000 |
| snowy owl conservation status | Least Concern (LC) | 200,000+ |
| south china tiger conservation status | Critically Endangered (CR) | 10 |
| southern white rhinoceros conservation status | Near Threatened (NT) | 18,000 |
| conservation status of orangutan | Critically Endangered (CR) | 55,000 |
| white rhino conservation status | Critically Endangered (CR) | 18,000 |
| wolverine conservation status | Near Threatened (NT) | 25,000 |
| african elephant conservation status | Vulnerable (VU) | 415,000 |
| african leopard conservation status | Vulnerable (VU) | 250,000 |
| african wild dog conservation status | Endangered (EN) | 6,000 |
| american bison conservation status | Near Threatened (NT) | 500,000 |
| amur leopard conservation status | Endangered (EN) | 80 |
| asian elephant conservation status | Endangered (EN) | 40,000 |
| basking shark conservation status | Vulnerable (VU) | 10,000+ |
| beaver conservation status | Least Concern (LC) | 10,000,000+ |
| bluefin tuna conservation status | Endangered (EN) | 20,000 |
| bull shark conservation status | Near Threatened (NT) | 100,000+ |
| conservation status of giraffes | Vulnerable (VU) | 68,000 |
| conservation status of snow leopard | Vulnerable (VU) | 4,000 |
| florida panther conservation status | Critically Endangered (CR) | 120 |
| frilled shark conservation status | Data Deficient (DD) | Unknown |
| glaucous macaw conservation status | Critically Endangered (CR) | 50 |
| great horned owl conservation status | Least Concern (LC) | 50,000+ |
| green sea turtle conservation status | Endangered (EN) | 25,000 |
| hawksbill sea turtle conservation status | Critically Endangered (CR) | 10,000 |
| hawksbill turtle conservation status | Critically Endangered (CR) | 10,000 |
| honey badger conservation status | Least Concern (LC) | 100,000+ |
| leatherback sea turtle conservation status | Vulnerable (VU) | 60,000 |
| leatherback turtle conservation status | Vulnerable (VU) | 60,000 |
| lions conservation status | Vulnerable (VU) | 20,000 |
| macaroni penguin conservation status | Least Concern (LC) | 500,000+ |